Guidance, ideas and examples to support schools in developing their curriculum, pedagogy, enrichment and support for more able learners, within a whole-school context of cognitively challenging learning for all. Includes ideas to support curriculum development, and practical examples, resources and ideas to try in the classroom. Popular topics include: curriculum development, enrichment, independent learning, questioning, oracy, resilience, aspirations, assessment, feedback, metacognition, and critical thinking.
Top tags:
pedagogy
questioning
enrichment
research
curriculum
oracy
independent learning
aspirations
cognitive challenge
free resources
KS3
KS4
language
critical thinking
assessment
English
literacy
feedback
metacognition
resilience
collaboration
maths
confidence
creativity
vocabulary
wellbeing
access
lockdown
mindset
problem-solving
  
|
Posted By Keith Watson FCCT,
22 March 2021
|
Dr Keith Watson, NACE Curriculum Development Director
What I Talk About When I Talk About Running by Haruki Murakami is one of my favourite books… even if reading it did not make me run faster. The title did, however, lead me to ask students: “What do you think about when you think about learning?” This is not an easy question to answer. We increasingly recognise the importance of developing metacognition in learning and the need to challenge pupils cognitively, but this is not always easy in the mixed ability classroom.
In the NACE report Making space for able learners – Cognitive challenge: principles into practice (2020), cognitive challenge is defined as “ how learners become able to understand and form complex and abstract ideas and solve problems”. We want students to achieve these high ambitions in their learning, but how is this achieved in a mixed ability class with increasing demands on the teacher, including higher academic expectations? The NACE report provides case studies showing where this has been achieved and highlights the common features across schools that are achieving this – and these key themes are worth reflecting upon. What do we mean by “challenge for all”?
“Challenge for all” is the mantra often recited, but is it a reality? At times it can appear that “challenge” is just another word for the next task. Or, perhaps, just a name for the last task. Working with teachers recently I asked: why do the more able learners need to work through all the preceding the tasks to get to the “challenge”? Are you asking them to do other work that is not challenging? Or coast until it gets harder? A month later the same teachers talked about how they now move those learners swiftly on to the more challenging tasks, noting that their work had improved significantly, they were more motivated and the learning was deeper. This approach also led to learners being fully engaged, meaning the teacher could vary the support needed across the class to ensure all pupils were challenged at the appropriate level.
“Teaching to the top” is another phrase widely used now and it is a good aspiration, although at times it is unclear what the “top” is. Is it grade 7 at GCSE or perhaps greater depth in Year 6? It is important to have these high expectations and to expose all learners to higher learning, but we need to remember that some of our learners can go even higher but also be challenged in ways that do not relate to exams. For instance, at Copthorne Primary School, the NACE report notes that “pupils are regularly set complex, demanding tasks with high-level discourse. Teachers pitch lessons at a high standard”. Note the reference to discourse – a key feature of challenge is the language heard in the classroom, whether from adults or learners. The “top” is not merely a grade; it is where language is rich and learning is meaningful, including in early years, where we often see the best examples.
Are your questions big enough?
The use of “low threshold, high ceiling” tasks are helpful in a mixed ability class, with all pupils able to access the learning and some able to take it further. In maths, a question as simple as “How many legs in the school?” can lead to good outcomes for all (including those who realise the question doesn’t specify human legs). But there is often a danger that task design can be quite narrow. The minutiae of the curriculum can push teachers to bitesize learning, which can be limiting – especially when a key aim has to be linking the learning through building schema. Asking “Big Questions” can extend learning and challenge all learners. The University of Oxford’s Oxplore initiative offers a selection of Big Questions and associated resources for learners to explore, such as “Should footballers earn more than nurses?” and “Can money buy happiness?”. There is a link to philosophy for children here, and in cognitively challenging classrooms we see deep thinking for all pupils. Can your learners build more complex schema?
All pupils need to build links in their learning to develop understanding, and more able learners can often build more detailed schema. To give a history example, understanding the break from Rome at the time of Henry VIII could be learned as a series of separate pieces of knowledge: marriage to Catherine of Aragon, the need for a male heir, wanting a divorce in order to marry Anne Boleyn, the religious backdrop, etc. Knowing these items is one thing, but learners need to make links between them and create a schema of understanding. The more able the pupil, the more links can be made, again deepening understanding. That is why in cognitively challenging classrooms skilled teachers ask questions such as:
- What does that link to?
- What does that remind you of?
- When have you seen this before?
- What is this similar to? Why?
These questions are especially useful in a busy mixed ability classroom. Prompt questions like these can be used in a range of situations, rather than always requiring another task for the more able pupil who has “finished”. (As if we have ever really finished)
Are you allowing time for “chunky” problems?
So, what else provides challenge? The NACE report notes: “At Portswood Primary School pupils are given ill-structured problems, chunky problems, and compelling contexts for learning”. Reflecting upon the old literacy hour, I used to joke: “Right Year 5, you have 20 minutes to write like Charles Dickens. Go!” How could there be depth of response and high-level work in such short time scales? What was needed were extended tasks that took time, effort, mistakes, re-writes and finally resolution. The task often needed to be chunky. Some in the class will need smaller steps and perhaps more modelling from the teacher, but for the more able learners their greater independence allows them to tackle problems over time.
This all needs organising with thought. It does not happen by accident. With this comes a sense of achievement and a resolution. Pupils are challenged cognitively but need time for this because they become absorbed in solving problems. This also works well when there are multiple solution paths. In a mixed ability class asking the more able to find two ways to solve a problem and then decide which was the most efficient or most effective can extend thinking. It also calls upon higher-order thinking because they are forced to evaluate. Which method would be worth using next time? Why? Justify. This also emphasises the need to place responsibility with the learner. “At Southend High School for Boys, teachers are pushed to become more sophisticated with their pedagogy and boost pupils’ cognitive contribution to lessons rather that the teacher doing all the work”. In a mixed ability class this is vital. How hard are your pupils working and, more importantly, thinking?
I wrote in a previous blog post about how essential the use of cutaway is in mixed ability classes. Retrieval practice, modelling and explanation are vital parts of a lesson, but the question is: do all of the students in your class always need to be part of that? A similar argument is made here. More able learners are sometimes not cognitively challenged as much in whole-class teaching and therefore, on occasion, it is preferable for these pupils to begin tasks independently or from a different starting point.
As well as being nurturing, safe and joyful, we all want our classrooms to be cognitively challenging. This is a certainly not easy in a mixed ability class but it can be achieved. High expectations, careful task design and an eye on big questions all play a part, alongside the organisation of the learning. In this way our teaching can be improved significantly – far more than my running ever will be…
Related blog posts
Additional reading and support
Tags:
cognitive challenge
grouping
metacognition
problem-solving
questioning
research
Permalink
| Comments (0)
|
  
|
Posted By Keith Watson FCCT,
27 January 2021
|
Dr Keith Watson, NACE Associate
In recent years many new developments in teaching have been most welcome and have helped the shift towards a more research-informed profession. NACE’s recent report Making space for able learners – Cognitive challenge: principles into practice provides examples of strategies used for the design and management of cognitively challenging learning opportunities, including reference to Rosenshine’s Principles of Instruction (2010) which outline many of these strategies.
These principles of instruction are particularly influential in current teaching, which is pleasing to the many good teachers who have been used them for years, although they may not have attached that exact language to what they were doing. These principles are especially helpful for early career teachers, but like all principles they need to be constantly reflected upon. I was always taken by Professor Deborah Eyre’s reference to “structured tinkering” (2002): not wholesale change but building upon key principles and existing practice.
This is where “cutaway” comes in – another of the strategies identified in the NACE report, and one which I would like to encourage you to “tinker” with in your approach to ability grouping and ensuring appropriately challenging learning for all.
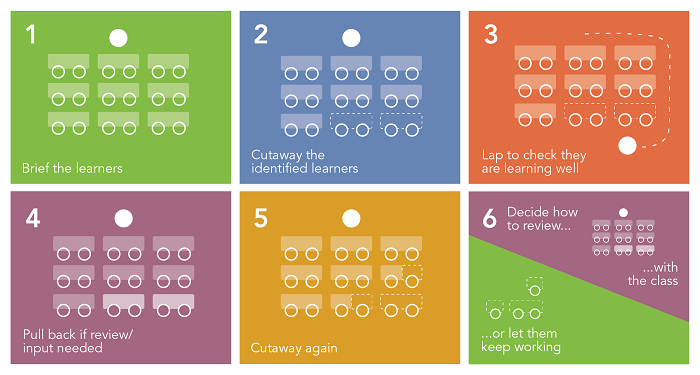
What is “cutaway” and why use it?
The “cutaway” approach involves setting high-attaining students off to start their independent work earlier than the vast majority of the class, while the teacher continues to provide direct instruction/ modelling to the main group. In this way the high attainers can begin their independent work more quickly and can avoid being bored by the whole class instruction which they can find too easy, even when the teacher is trying to “teach to the top”. Once the rest of the class has begun their independent work, the teacher can then focus on the higher attaining group to consolidate the independent work and extend them further.
There are more nuances which I will explain later, but you may wonder, how did this way of working come about?
An often-quoted figure from the National Academy of Gifted and Talented Youth (NAGTY) was that gifted students may already have acquired knowledge of 40-50% of their lessons before they are taught. If I am honest, this was 100% in some of my old lessons! With whole class teaching, retrieval practice tasks and modelling (all essential elements in a lesson), there are clear dangers of pupils being asked to work on things they already know well. There is the issue of what Freeman, (quoted in Ofsted, 2005:3), called the “three-time problem” where: “Pupils who absorb the information the first time develop a technique of mentally switching off for the second and the third, then switching on again for the next new point, involving considerable mental skill.” Why waste this time?
The idea of “cutaway” was consolidated when I carried out a research project involving the use of learning logs to improve teaching provision for more able learners (Watson, 2005). In this project teachers adapted their teaching based on pupil feedback. The teachers realised that, in a primary classroom, keeping the pupils too long “on the carpet” was inappropriate and the length of time available to work at a high level was being minimised. One of the teachers reflected: “Sometimes during shared work on the carpet, when revising work from previous lessons to check the understanding of other pupils, I feel aware of the more able children wanting to move on straight away and find it difficult to balance the needs of all the children within the Year 5 class.”
It therefore became common in lessons (though not all lessons) to cutaway pupils when they were ready to begin independent work. By using “cutaway” the pupils use time more effectively, develop greater independence, can move through work more quickly and carry out more extended and more challenging tasks. The method was commented upon favourably during a HMI inspection that my school received and has ever since been a mainstay of teaching at the school.
Who, when and how to cutaway
So how does a teacher decide when and who to cutaway? The method is not needed in all lessons, the cutaway group should vary based upon AfL, and at its best it involves pupils deciding whether they feel they need more modelling/explanation from the teacher or are ready to be cutaway. In a recent NACE blogpost on ability grouping, Dr Ann McCarthy emphasises that in using cutaway “the teacher constantly assesses pupils’ learning and needs and directs their learning to maximise opportunities, growth and development” and pupils “leave and join the shared learning community”. This underlines the importance of the AfL nature of the strategy and the importance of developing learners’ metacognition, which was another key finding in the NACE report.
Sometimes the cutaway approach is decided on before a lesson by the teacher based upon previous work. In GCSE history, a basic retrieval task on the Norman invasion could be time wasted for a more able pupil who has secure knowledge, whereas being cutaway to do an independent task centred on the role of the Pope in supporting William would be more challenging and worthwhile. It comes down to one key question a teacher needs to ask themselves when speaking to the whole class: “Who do I need here now?” Who needs to retrieve this knowledge? Who needs to hear this explanation? Who needs to see this model or complete this example? If a small group of higher attainers do not need this, then why slow the pace of their learning? Why not start them either on the same work independently or more challenging work to accelerate learning?
Why not play around with this idea? Explain your thinking to the pupils and see how they respond. Sometimes, at the end of one lesson, a task for the next lesson can be explained and the pupils could start the next lesson by working on that task straight away. The 2015 Ofsted handbook said, “The vast majority of pupils will progress through the programmes of study at the same rate”, and ideally, they will. However, a few pupils will progress at a faster rate and therefore need adapted provision. The NACE research and accompanying CPD programme suggests the use of “cutaway” can achieve this and it is well worth all teachers doing some “structured tinkering” with this strategy.
References
Additional reading and support
Share your views
How do you use ability grouping, and why? Share your experiences by commenting on this blog post or by contacting communications@nace.co.uk
Tags:
cognitive challenge
differentiation
grouping
independent learning
pedagogy
research
Permalink
| Comments (0)
|
  
|
Posted By Ann McCarthy,
06 January 2021
|
Dr Ann McCarthy, NACE Associate and co-author of NACE’s new publication “Cognitive challenge: principles into practice”.
To group or not to group: that is the question…
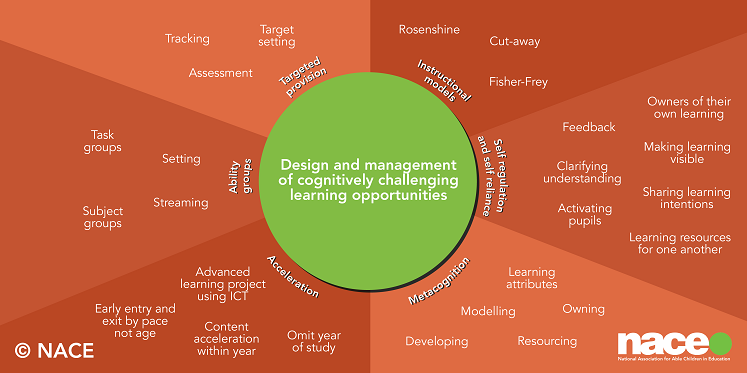
The organisation and management of cognitively challenging learning environments is one of three focus areas highlighted in NACE’s new research publication, “Cognitive challenge: principles into practice”, which marks the first phase in our “Making Space for Able Learners” project. Developed in partnership with NACE Challenge Award-accredited schools, the research examines the impact of cognitive challenge in current school practice against a backdrop of relevant research.
As teachers, we aim to provide a cognitively challenging learning environment for our more able and exceptionally able pupils, which is beneficial to them. The organisational decisions surrounding this should therefore optimise opportunities for learning. Teachers and school leaders must not only consider content to be studied, but also the impact of classroom management decisions from the perspective of the learner. The NACE research showed that these classroom management and organisational decisions were one of three key factors impacting on cognitively challenging learning, alongside curriculum organisation and design and the use of rich and extended talk and cognitive discourse.
 One aspect of managing cognitively challenging learning environments is any choice relating to mixed ability teaching versus a variety of designs for selection and grouping by ability. Within the classroom the teacher also balances demands to provide opportunities for all, while simultaneously identifying the nature and opportunity for challenge.
Does ability grouping benefit learners?
There is a paucity of strong evidence that ability grouping is beneficial to academic outcomes for all. However, Parsons and Hallam (2014) did find that grouping can benefit more able pupils. This benefit is not necessarily associated with the act of setting, but with the quality of teaching provided for these groups. Pupils also have opportunities to work at a faster pace, but against this aspiration, Boaler et al. (2000) found pace incompatible with understanding for many pupils. Regardless of the choice made to group or not to group, there is a need to reflect on whether teaching is homogenous or designed to meet the needs of the pupils. Often the weakness is the assumption that grouping alone will drive the learning experience, without an understanding of the cognitive and emotional impact this has on the pupils themselves.
The Education Endowment Foundation (EEF) has examined the use of setting and streaming, which are usually related to attainment rather than ability, and has found that there is often a small negative impact for disadvantaged pupils and lower abilities. When designing learner groupings, it is important to be aware of the impact for all learners and create a beneficial model for all.
How should teachers and schools approach ability grouping?
First, decide what you hope to teach and what it is pupils have the potential to achieve, given enough learning opportunities. Remember, learning is not limited to reproducing planned content by rote, but instead its success lies within a growth of knowledge, its complexity, and its application. Pupils bring a wide range of prior learning, knowledge and experiences which they can share with each other and use to construct new schema. In a well-designed learning environment, pupils have the potential to develop their knowledge, skills and understanding beyond the delivered content. Young et al. (2014) demonstrate the importance of powerful knowledge which takes pupils beyond their own experiences. The development of metacognition and exposure to wider experience should therefore be included in decisions related to the organisation of groups and lesson planning.
Second, decide what environment will provide the best learning experience for the pupils.
- Is it best to present advanced curricula at an accelerated rate?
- Does teaching include multiple high-order thinking models and skills?
- Is learning pupil-centred?
- Are multiple modality enquiry methods in play?
- Will grouping take account of the complexity of ability and enhance its manifestation?
- Will pupils benefit from a wide range of perspectives?
- Will pupils utilise the learning experiences of others to reflect upon and refine their own learning?
The answers to these questions will help teachers to make decisions regarding the nature of grouping and classroom organisation. The choice of model should be one which most benefits the learner, one which is not driven by systemic organisational requirements, and one which recognises the impact of external factors on perceived ability.
Finally, what models are available and how can cognitive challenge be achieved within them?
- Mixed ability grouping has the benefit of exposing pupils to the wider knowledge, background, and experience of others. In these environments, problems with different layers of complexity and multiple learning routes are often used. The big question or cognitively challenging proposition often promotes the learning with supporting systems and prompts in place for those challenged by the learning.
- Cutaway models are an alternative to the simpler mixed ability model. In the cutaway approach, the teacher constantly assesses pupils’ learning and needs and directs their learning to maximise opportunities, growth, and development. Pupils join and leave the shared learning (“cutting away” as appropriate), based on prior learning and their response to the existing task. This model develops and utilises independence and metacognition.
- Grouping by task is often used when it is possible to create smaller groups working on different tasks within the same classroom. The teacher uses very specific knowledge relating to pupils’ prior learning and abilities to organise the classroom groups. The teacher can therefore target the teaching to respond to more specific learning opportunities, which in turn can increase pupils’ enjoyment and engagement in their learning.
- Grouping by subject is an extension of grouping by task. If pupils learn all their subjects within the same class group, this enables the teacher to note the different strengths within the subject. In larger schools, pupils are often grouped by overall performance in specific subjects. This model might include advanced curriculum and require higher-order thinking skills. Pupils might be given opportunities to research more deeply into areas of interest. For this model to be successful there needs to be fluidity between the groups so that pupils are well-placed to enjoy cognitively challenging experiences.
With these ideas in mind, schools will then create an overarching model which reflects the school vision, ethos and culture. Teachers will consistently strive to provide cognitively challenging learning opportunities which benefit all. They use their knowledge of the pupils’ past and present learning and their vision of what the pupils can be and can achieve in the future to design the learning environment. They then organise the classroom to excite, engage and challenge their pupils – remembering that regardless of the sophistication of the approach, every group will be mixed ability as no two pupils are identical. If high-quality and engaging teaching is child-centred and not homogenous, then pupils will excel in cognitively challenging classrooms.
References
- Boaler, J., Wiliam, D. and Brown, M. (2000). Students’ experiences of ability grouping – disaffection, polarisation and the construction of failure. British Education Research Journal, 26 (5), 631–648.
- Education Endowment Foundation, Teaching and Learning Toolkit
- Parsons, S. and Hallam, S. (2014). The impact of streaming on attainment at age seven: evidence from the Millennium Cohort Study. The Oxford Review of Education, 40 (5), 567-589.
- VanTassel-Baska, J. and Brown, E. (2007) Toward Best Practice: An analysis of the efficacy of curriculum models in gifted education. Gifted Child Quarterly, 52, 342.
- Young, M and Muller, J. (2013). On the Powers of Powerful Knowledge. Review of Education1(3) 229-250.
Additional reading and support
Share your views
How do you use ability grouping, and why? Share your experiences by commenting on this blog post or by contacting communications@nace.co.uk
Tags:
cognitive challenge
CPD
differentiation
grouping
leadership
pedagogy
research
Permalink
| Comments (0)
|
|