Guidance, ideas and examples to support schools in developing their curriculum, pedagogy, enrichment and support for more able learners, within a whole-school context of cognitively challenging learning for all. Includes ideas to support curriculum development, and practical examples, resources and ideas to try in the classroom. Popular topics include: curriculum development, enrichment, independent learning, questioning, oracy, resilience, aspirations, assessment, feedback, metacognition, and critical thinking.
Top tags:
pedagogy
questioning
enrichment
research
curriculum
oracy
independent learning
aspirations
cognitive challenge
free resources
KS3
KS4
language
critical thinking
assessment
English
literacy
feedback
metacognition
resilience
collaboration
maths
confidence
creativity
vocabulary
wellbeing
access
lockdown
mindset
problem-solving
  
|
Posted By Lol Conway,
06 May 2025
|
Lol Conway, Curriculum Consultant and Trainer for the Design and Technology Association
Throughout my teaching, inclusivity has always been at the forefront of my mind – ensuring that all students can access learning, feel included, and thrive. Like many of my fellow teachers, at the start of my teaching career my focus was often directed towards supporting SEND or disadvantaged students, for example. I have come to realise, to my dismay, that more able students were not high up in my consideration. I thought about them, but often as an afterthought – wondering what I could add to challenge them. Of course, it should always be the case that all students are considered equally in the planning of lessons and curriculum progression and this should not be dictated by changes in school data or results. Inclusivity should be exactly that – for everyone.
True inclusivity for more able students isn’t about simply adding extra elements or extensions to lessons, much in the same way that inclusivity for students with learning difficulties isn’t about simplifying concepts. Instead, it’s about structuring lessons from the outset in a way that ensures all students can access learning at an appropriate level.
I realised that my approach to lesson planning needed to change to ensure I set high expectations and included objectives that promoted deep thinking. This ensured that more able students were consistently challenged whilst still providing structures that supported all learners. It is imperative that teachers have the confidence and courage to relentlessly challenge at the top end and are supported with this by their schools.
As a Design and Technology (D&T) teacher, I am fortunate that our subject naturally fosters higher-order thinking, with analysis and evaluation deeply embedded in the design process. More able students can benefit from opportunities to tackle complex, real-world problems, encouraging problem-solving and interdisciplinary connections. By integrating these elements into lessons, we can create an environment where every student, including the most able, is stretched and engaged. However, more often than not, these kinds of skills are not always nurtured at KS3.
Maximizing the KS3 curriculum
The KS3 curriculum is often overshadowed by the annual pressures of NEA and examinations at GCSE and A-Level, often resulting in the inability to review KS3 delivery due to the lack of time. However, KS3 holds immense potential. A well-structured KS3 curriculum can inspire and motivate students to pursue D&T while also equipping them with vital skills such as empathy, critical thinking, innovation, creativity, and intellectual curiosity.
To enhance the KS3 delivery of D&T, the Design and Technology Association has developed the Inspired by Industry resource collection – industry-led contexts which provide students with meaningful learning experiences that go beyond theoretical knowledge. We are making these free to all schools this year, to help teachers deliver enhanced learning experiences that will equip students with the skills needed for success in design and technology careers.
By connecting classroom projects to real-world industries, students gain insight into the practical applications of their learning, fostering a sense of purpose and motivation. The focus shifts from achieving a set outcome to exploring the design process and industry relevance. This has the potential to ‘lift the lid’ on learning, helping more able learners to develop higher-order skills and self-directed enquiry.
These contexts offer a diverse range of themes, allowing students to apply their knowledge and skills in real-world scenarios while developing a deeper understanding of the subject and industry processes. Examples include:
- Creating solutions that address community issues such as poverty, education, or homelessness using design thinking principles to drive positive change;
- Developing user-friendly, inclusive and accessible designs for public spaces, products, or digital interfaces that accommodate people with disabilities;
- Designing eco-friendly packaging solutions that consider materials, manufacturing processes, and end-of-life disposal.
These industry-led contexts foster independent discovery and limitless learning opportunities, particularly benefiting more able students. By embedding real-world challenges into the curriculum, we can push the boundaries of what students can achieve, ensuring they are not just included but fully engaged and empowered in their learning journey.
Find out more…
NACE is partnering with the Design & Technology Association on a free live webinar on Wednesday 4 June 2025, exploring approaches to challenge all learners in KS3 Design & Technology. Register here.
Tags:
access
cognitive challenge
creativity
design
enquiry
free resources
KS3
myths and misconceptions
pedagogy
problem-solving
project-based learning
technology
Permalink
| Comments (0)
|
  
|
Posted By Amanda Hubball,
30 January 2025
|
Amanda Hubball, Deputy Head and More Able Lead at Alfreton Nursery School, outlines the use of “thinking booklets” to embed challenge into the early years setting.
At Alfreton Nursery School, staff believe that children need an intrinsic level of challenge to enhance learning. This challenge is not always based around adding symbols to a maths problem or introducing scientific language to the magnet explorations. An early years environment has countless opportunities for challenge and this challenge can be provided in creative ways.
Thinking booklets: invitations to think and talk
Within the nursery environment, Alfreton has created curriculum zones. These zones lend themselves to curriculum progression, whilst also providing a creative thread of enquiry which runs through all areas. Booklets can be found in each space and these booklets ask abstract questions and offer provocations for debate. Drawing on the pedagogical approach Philosophy for Children (p4c), we use these booklets to ensure classroom spaces are filled with invitations to think and talk.
Literacy booklets
Booklets within the literacy area help children to reflect on the concepts of reading and writing, whilst promoting communication, breadth of vocabulary and the skills to present and justify an opinion.

For example, within the “Big Question: Writing” booklet, staff and children can find the following questions:
- What is writing?
- If nobody could read, would we still need to write?
 Alongside these and other questions, there are images of different types of writing. Musical notation, cave drawings, computer text and graffiti to name but a few. Children are empowered to discuss what their understanding of writing actually is and whether others think the same. Staff are careful not to direct conversations or present their own views. Alongside these and other questions, there are images of different types of writing. Musical notation, cave drawings, computer text and graffiti to name but a few. Children are empowered to discuss what their understanding of writing actually is and whether others think the same. Staff are careful not to direct conversations or present their own views.
Maths booklets
Maths booklets are based around all aspects of the subject: shape, size, number. . .
- If a shape doesn’t have a name, is it still a shape?
- What is time?
- If you could be a circle or a triangle, which would you choose and why?
Questions do not need to be based around developing subject knowledge, and the more abstract and creative the question, the more open to all learners the booklets become.
Children explore the questions and share views. On revisiting these questions another day, often opinions will change or become further embellished. Children become aware that listening to different points of view can influence thinking.

Creative questions
Developing the skills of abstract thought and creative thinking is a powerful gift and children enjoy presenting their theories, whilst sometimes struggling to understand that there is no right or wrong answer. For the more analytical thinkers, being asked to consider whether feelings are alive – leading to an exploration of the concept “alive” – can be highly challenging. Many children would prefer to answer, “What is two and one more?”
Alfreton Nursery School’s culture of embracing enquiry, open mindset and respect for all supports children’s levels of tolerance, whilst providing cognitive challenge and opportunities for aspirational discourse. The use of simple strategies to support challenge in the classroom ensures that challenge for all is authentically embedded into our early years practice.
Read more from Alfreton Nursery School:
Tags:
cognitive challenge
critical thinking
curriculum
early years foundation stage
enquiry
oracy
pedagogy
philosophy
questioning
Permalink
| Comments (2)
|
  
|
Posted By Oliver Barnes,
04 December 2024
|
Ollie Barnes is lead teacher of history and politics at Toot Hill School in Nottingham, one of the first schools to attain NACE Challenge Ambassador status. Here he shares key ingredients in the successful addition of a module on Hong Kong to the school’s history curriculum. You can read more in this article published in the Historical Association’s Teaching History journal.
When the National Security Law came into effect in Hong Kong, it had a profound and unexpected impact 6000 miles away, in Nottinghamshire’s schools. Important historical changes were in process and pupils needed to understand them. As a history department in a school with a growing cohort of Hong Kongers, it became essential to us that students came to appreciate the intimate historical links between Hong Kong and Britain and this history was largely hidden, or at least almost entirely absent, in the history curriculum.
But exploring Hong Kong gave us an opportunity to tell our students a different story, explore complex concepts and challenge them in new ways. Here I will outline the opportunities that Hong Kong can offer as part of a broad and diverse curriculum.
Image source: Unsplash
1. Tell a different story
In our school in Nottinghamshire, the student population is changing. Since 2020, the British National Overseas Visa has allowed hundreds of families the chance to start a new life in the UK. Migration from Hong Kong has rapidly increased. Our school now has a large Cantonese-speaking cohort, approximately 15% of the school population. The challenge this presented us with was how to create a curriculum which is reflective of our students.
Hong Kong offered us a chance to explore a new narrative of the British Empire. In textbooks, Hong Kong barely gets a mention, aside from throwaway statements like ‘Hong Kong prospered under British rule until 1997’. We wanted to challenge our students to look deeper.
We designed a learning cycle which explored the story of Hong Kong, from the Opium Wars in 1839 to the National Security Law in 2020. This challenged our students to consider their preconceptions about Hong Kong, Britain’s impact and migration.
2. Use everyday objects
To bring the story to life, we focused on everyday objects, which are commonly used by our students and could help to tell the story.
First, we considered a cup of tea. We asked why a drink might lead to war? We had already explored the Boston Tea Party, as well as British India, so students already knew part of this story, but a fresh perspective led to rich discussions about war, capitalism, intoxicants and the illegal opium trade.
Our second object was a book, specifically Mao’s Little Red Book. We used it to explore the impact of communism on China, showing how Hong Kong was able to develop separately, with a unique culture and identity.
Lastly, an umbrella. We asked: how might this get you into trouble with the police? Students came up with a range of uses that may get them arrested, before we revealed that possessing one in Hong Kong today could be seen as a criminal act. This allowed us to explore the protest movement post-handover.
At each stage of our enquiry, objects were used to drive the story, ensuring all students felt connected to the people we discussed.
Umbrella Revolution Harcourt Road View 2014 (Source: Wikimedia Commons)
3. Keep it complex
In order to challenge our students, we kept it complex. They were asked to draw connections and similarities between Hong Kong and other former British colonies. We also wanted them to encounter capitalism and communism, growth and inequality. Hong Kong gave us a chance to do this in a new and fresh way.
Part of this complexity was to challenge students’ preconceptions of communism, and their assumptions about China. By exploring the Kowloon walled city, which was demolished in 1994, students could discuss the problems caused by inequality in a globalised capitalist city.
Image source: Unsplash
What next?
Our Year 9 students responded overwhelmingly positively. The student survey we conducted showed that they enjoyed learning the story and it helped them understand complex concepts.
Hong Kong offers curricula opportunities beyond the history classroom. In English, students can explore the voices of a silenced population, forced to flee or face extradition. In geography, Hong Kong offers a chance to explore urbanisation, the built environment and global trade.
Additional reading and resources
Tags:
cognitive challenge
critical thinking
curriculum
enquiry
history
KS3
pedagogy
Permalink
| Comments (0)
|
  
|
Posted By Tom Stewart,
01 April 2022
|
Tom Stewart, Head of History at Maiden Erlegh School, sets out tangible strategies that he and his department take when challenging more able students in history lessons.
History at secondary school level is a subject that, from my experience, is usually taught in mixed ability classes. Due to this, and to rightfully ensure the progress of those who struggle with literacy and require further support, lessons can tend to be pitched towards the middle with scaffolding and structure in place to help those struggling. The potential problem with this approach is that it risks neglecting the more able students and those who need to be challenged or stretched (or whichever phrase is used in your setting), to reach their potential. I hope this blog post will give you some ideas to take away to challenge the more able learners in your history lessons.
#1. Short-term: Questioning
A simple and easy way to challenge those more able students is through effective use of the questioning they face in a lesson. I imagine most teachers know about open and closed questions and how the latter can limit students to a one-word answer, whilst the former can require students to elaborate in more depth. Therefore, the answer the students give can often depend on how much thought has gone into the question asked.
It is important to consider why a teacher is asking a question and this can then be applied to challenging the more able students by asking a variety of questions for different reasons. In a recent CPD session at my school, delivered by two excellent Assistant Headteachers, Rob Buck and Ben Garner, this principle, with some examples, was shared with staff (Figure 1). It reminded myself and my department to think carefully about the questioning we carried out and to target those more able students, whether they be in Year 7, Year 10 or Year 13.
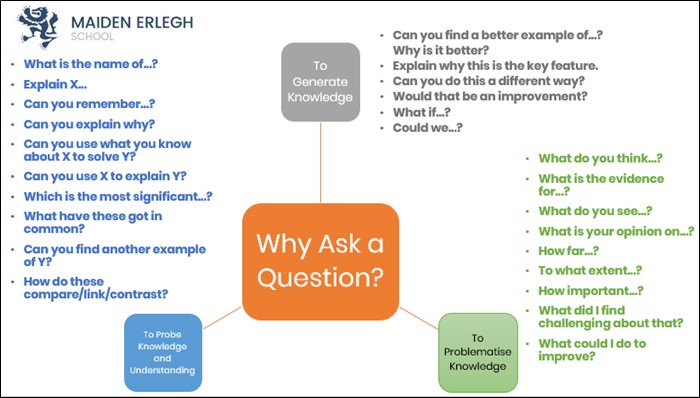
Figure 1
#2. Medium-term: Widen their perspectives
More able students are often characterised by a curious and inquisitive nature. To support this, it is important to not be overly selective with the history shared with students, but find opportunities to reveal more of the story. Students of all abilities enjoy learning knowledge that isn’t necessarily vital to the topic – knowledge that Bailey-Watson calls ‘hinterland’ knowledge – and we should be willing to share with students more of the big picture in order to widen their perspectives and improve their historical thinking.
Homework can be an outlet for this; the previously mentioned Bailey-Watson and Kennet launched their ‘meanwhile, elsewhere…’ project (Figure 2) with the explicit intention of ‘expanding historical horizons’. Used effectively, this is a strategy that challenges the more able students to make those links between what they know and what they are yet to know.

Figure 2
#3. Long-term: Enquiry-based topics
History lends itself to a wealth of interesting topics. This selection narrows at GCSE and A-Level as specifications force middle leaders to select one topic and not another. However, at Key Stage 3, there is normally more choice and also an opportunity to challenge more able students. We have found evolving already-established topics – or creating new ones where time allowed and necessity demanded – into enquiry-based ones supports more able students by forcing them to ‘think hard’.
Our topic on the Norman Conquest, an event described by Peter Rex as ‘the single most important event in English history’ avoids a simpler narrative of events and instead forces students, especially the more able, to consider how King William managed not only to gain control but maintain it after the Battle of Hastings (Figure 3). This topic was designed by my fantastic colleague, Chloe Bateman, and this approach provides all students with an overview of where the lesson and topic fits in and also encourages deep thinking about the answer to the enquiry question before it has even been covered.
Combined with sharing demanding texts with students in lessons and homework that relates directly to the enquiry question, whilst extending their knowledge and understanding even further, enquiry-based topics can prove very effective at challenging more able students in secondary history.
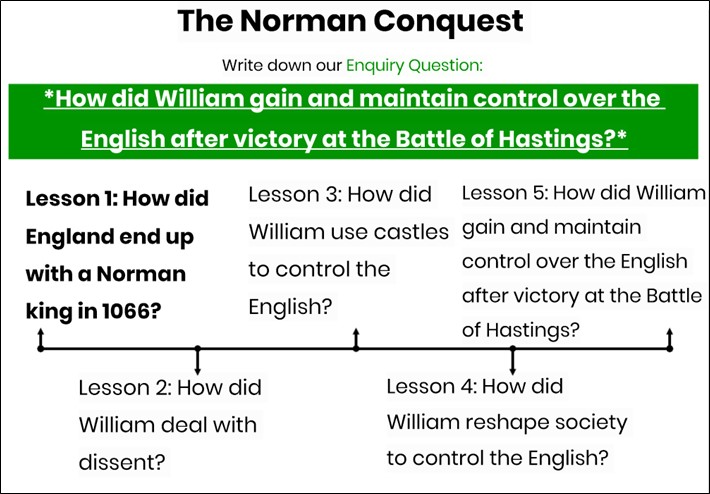
Figure 3
There are plenty of strategies out there and there are more that I use and could have shared with you, but here are three that you could look to introduce to your setting. The important point is to be mindful about the experience more able students get in our classrooms. Do they feel challenged? Would you in their shoes? If not, then be active in doing something about it.
References
- Bailey-Watson, W. and Kennett, R. (2019). '"Meanwhile, elsewhere…": Harnessing the power of community to expand students’ historical horizons’, Teaching History, 176.
- https://meanwhileelsewhereinhistory.wordpress.com/
- Paramore, J. (2017). Questioning to Stimulate Dialogue, in Paige R., Lambert, S. and Geeson, R. (eds), Building Skills for Effective Primary Teaching, London: Learning Matters.
- Rex, P. (2011). 1066: A New History of the Norman Conquest, Amberley Publishing.
Read more:
Tags:
enquiry
history
humanities
KS3
KS4
KS5
questioning
Permalink
| Comments (0)
|
  
|
Posted By Ilona Bushell,
28 March 2022
Updated: 22 March 2022
|
Ilona Bushell, Assistant Editor at The Day
Telling the truth about the world we share has become one of the heroic endeavours of the age amidst an ever-changing digital tsunami of information. Effectively embedding journalism in your school is vital to equip young citizens with the skills needed to develop a healthy worldview, engage in a democratic society and tackle the world’s biggest challenges, leading the way to a brighter future.
There is no doubt that news literacy helps develop skills that are valuable right across the curriculum – and prepares children for their adult life. As these young people become voters, tax-payers and earners, they will have the basic tools to navigate the noise, confusion and fog of reality.
Here at the online newspaper for schools, The Day, we call the regular consumption of news a “real-world curriculum”. In February 2022 we launched The Global Young Journalist Awards (GYJA), a free competition open to all under 18s around the world. We aim to inspire young people to build a better world through storytelling, and the ambition is for GYJA to become the leading award for youth journalism. What, why, and why now?
Written entries are welcome, but the awards are open to work in any medium – including video, photo, audio, graphic or podcast – opening up the floor to different student abilities and areas of interest. The aim is to showcase a variety of voices and encourage young people to report on what truly matters to them.
American actor and comedian Tina Fey, who will be among the panel of GYJA judges, said, “There has never been a more important time to get young people involved in truth-seeking. It is vital for our future that journalists investigate without fear or favour, and this competition is an excellent way of inspiring children to get involved.”
The judging panel also includes TV broadcaster Ayo Akinwolere, the BBC’s gender and identity correspondent Megha Mohan, the FT’s top data journalism developer Ændra Rininsland, and Guardian columnist Afua Hirsch.
Indian computer scientist and educational theorist Sugata Mitra sees the awards as an opportunity to see glimpses of unexplored minds: “I have found children to be good at making up things. They can assemble all sorts of information into stories that are, at worst, fascinating and, at best, brutally honest. A journalist that can think like a nine-year-old will be astonishing… Can nine-year-olds think like a journalist?”
How are the awards aligned to school curricula?
There is an explosion of great reporting today on topics relevant to every area of the school curriculum. The award categories listed below are designed to fit within students’ areas of study and contribute to a rich real-world curriculum. Through their storytelling, entrants can build on important skills including communication, research, fact-checking, confidence, literacy, oracy, individuality and empathy.
GYJA categories:
1. Campaigning journalist of the year
2. Interviewer of the year
3. International journalist of the year
4. Political journalist of the year
5. Mental health journalist of the year
6. Environment journalist of the year
7. Science & technology journalist of the year
8. Race & gender journalist of the year
9. Sports journalist of the year
10. Climate journalist of the year (primary only)
How can schools get involved?
Teachers can download the Awards entry pack at www.theday.co.uk/gyja2022. The entry pack and website include a host of free resources for students. There are top tips from sponsors and judges, prompt ideas, best practice examples and guidance on the six journalistic formats they can use. What’s in store for the winners?
Winners will be announced at a live virtual ceremony in June. Award winners will have their words, video, photo, graphic or podcast published on The Day’s website and be given the chance to connect with role models from the world of media and current affairs.
Winners will be invited to join The Day’s Student Advisory Board for a year, while winners and runners-up will be offered a day’s work experience in a national newsroom and receive trophies.
Competition sponsors include The Fairtrade Foundation, The Edge Foundation, Oddizzi, Brainwaves, National Literacy Trust and Hello World.
About The Day
The Day is a digital newspaper for use in schools and colleges. It has a daily average circulation of 378,000 students, the largest readership among those aged 18 and under of any news title. Over 1,300 schools are subscribers. NACE members can benefit from a 20% discount on subscriptions to The Day; for details of this and all NACE member offers, log in and visit our member offers page.
Tags:
competitions
critical thinking
English
enquiry
free resources
independent learning
literacy
research
student voice
Permalink
| Comments (0)
|
  
|
Posted By Daisy Morley,
28 March 2022
Updated: 22 March 2022
|
Daisy Morley, primary teacher and history lead at Calcot Schools, outlines her approach to identifying and challenging more able learners in history – building historical knowledge, understanding and enquiry skills.
As a teacher it currently seems to me that a lot of attention is given to the children who need to meet age-related expectations. While these pupils’ needs are important and their needs must be met, this focus can mean that greater depth and ‘more able’ pupils are often forgotten. It is essential that more able learners are not neglected and are given ample opportunities to showcase their knowledge and shine.
History is one subject where, through careful consideration and planning, more able learners can thrive. Within this blog post, I will examine how to identify and challenge more able learners in history, in the context of primary teaching. These thoughts derive from personal experiences and from extensive research on the relevant literature and recent Ofsted reports. I will focus on ‘historical knowledge’, ‘historical understanding’ and ‘historical enquiry’ in order to suggest how we can think about challenging more able learners in history.
More able in history or just literacy?
Often, children whose strength lies in history will find that they are confident in literacy. Although strong literacy skills will greatly benefit their ability to share, form and communicate their ideas and findings, this does not necessarily mean that they are or will be more able historians. Interestingly, I think that the personal interests of children play a pivotal part in whether they have excelled in history beyond their age-related expectations. This is true from children as young as Year 1, to pupils nearing the end of their primary education. As educators, particularly if you are a subject leader, it is essential that time is taken to identify those children with a personal interest in history, and to provide them with opportunities to showcase their knowledge.
The building blocks: historical knowledge
First and foremost, the subject of history is rooted in knowledge; it is a knowledge-based subject (Runeckles, 2018: 10). While it is essential that pupils’ analytical skills are developed, this cannot be done without first ensuring that all pupils have a secure grounding in historical knowledge. This is also made clear in recent literature from Ofsted inspectors. Tim Jenner, HMI, Ofsted’s subject lead for history, has stated that when teaching history there must be an emphasis placed on content and knowledge (Jenner, 2021). In the most recent Ofsted reports, the term ‘knowledge’ has been divided into knowledge of ‘substantive concepts’, which relates to broader concepts, such as empire, monarch and economy, and ‘chronological knowledge’, which refers to the broader concepts within history, such as the key features of Anglo-Saxon England (Jenner, 2021).
The National Curriculum does expect pupils to “understand the methods of historical enquiry, including how evidence is used rigorously to make historical claims, and discern how and why contrasting arguments and interpretations of the past have been constructed” (DFE, 2013). The enquiry and analytical skills required to thrive in history are essential. However, these skills cannot be developed without first imparting the key historical knowledge to children.
Facts are the building blocks of history.
To emphasise this point, let us look at an example. Imagine a teacher wants to include a module on Boudicca in their history curriculum. Boudicca is listed in the National Curriculum for History under a non-statuary example, and has crucial ties with the statuary module on the Roman Empire and its impact on Britain. For the pupils to understand Boudicca’s historical significance, they would first need to have a secure grasp of the key features of the Roman Empire. Following this, they would then need to be taught the key components of Britain during this time. This knowledge would be essential before embarking on a specialised study of Boudicca. If the teacher then wished to hone and develop pupils’ analytical and enquiry skills, they could include a lesson on the conflicting sources that are available regarding Boudicca. To understand the primary written sources, however, they would first need to have a secure understanding of the historical knowledge of Boudicca, the Roman Empire, and the political landscape of Britain during this time.
Building historical knowledge takes time, as it requires a build-up of knowledge. As a result, educators may not see this accumulation of knowledge until a significant period of learning time has passed. Nevertheless, for children to develop their enquiry skills, historical knowledge is essential.
Developing historical understanding through open-ended questions
To see progression within a pupil’s historical understanding, historical knowledge, understanding and enquiry are best taught alongside one another. Historical knowledge and understanding are inextricably linked, and it would be difficult to separate these concepts within every lesson. Nevertheless, if a child is demonstrating the potential to achieve beyond the age-related expectations in history, their historical understanding could be one way to identify this – and thus to extend and challenge their learning. More able learners often process the key historical knowledge more quickly than their peers, which in turn means that they often quickly grasp the role of criteria in formulating and articulating an historical explanation or argument. Furthermore, more able learners are frequently able to draw generalisations and conclusions from a range of sources of evidence. One way to identify this could be ensuring that teachers ask open-ended questions, as the answers that children arrive at depend largely on questions asked.
I try to implement these open-ended questions in lessons, particularly across Key Stage 2. One approach which has worked particularly well came to light in a Year 3 lesson on “What did the diet of a typical Stone Age person encompass in prehistoric Britain?” This lesson relied on enquiry-based learning, which, although sometimes more difficult to deliver, lent itself well to inputting open-ended questions and highlighted the investigative nature of history. The children were given ‘organic evidence’ (pretend human waste), which pivoted around unpicking evidence and how historians use different types of evidence to find out about the past.
From this lesson, after unpicking our evidence, all of the children were able to deduce that prehistoric people ate nuts, seeds and berries. Pupils with a more advanced understanding were able to conclude that prehistoric inhabitants had to find food for themselves and that this is one of the reasons people from that time are called ‘hunter-gatherers’, because they had to hunt and gather their food.
For the children who had already come to the conclusions about hunter-gatherers, I asked more open-ended questions, which required them to draw their own conclusions, using the evidence that had been assessed, including “What about the meat?”, “Why haven’t we found meat in the organic evidence?” Some of these children were able to utilise their knowledge from previous lessons on Stone Age Britain and concluded that there were certain dangers in finding meat. They explained that people had to kill the animal and prepare it themselves, which was dangerous. One child even went on to say that meat also rots and that may have been why there was no surviving meat within the evidence. Although these open-ended questions help to stretch the more able learners, it does require teachers to direct the more challenging questions to the correct pupils, which relies on teachers knowing which of the pupils are excelling in history.
Making links: developing historical enquiry skills
I often find that historical enquiry skills are the hardest to master. From teaching this within lessons, it seems the key component to identifying the more able learners in history is to identify whether the pupils can link history together. Can they use their knowledge to comment on how the lives of people from the past have changed over time? Can they identify trends and commonalities between contemporary cultures? Do they notice how key changes transformed the lives and the culture of a particular civilisation? Perhaps most essentially, can the more able children use their historical knowledge and understanding to draw conclusions on events, people and places from the past? This relies on a pupil being able to problem-solve and reason with evidence, and apply this knowledge in order to evaluate the evidence in question.
Below is an example of a child’s work. The lesson was titled “What was bronze used for?”

I have chosen this example because this pupil was able to link their knowledge together, to form their own conclusions, which were based on key factual knowledge. For example, this child independently came to the conclusion that because their weapons were better, their quality of life improved. Amazingly, this pupil also commented on the fact that people from the Bronze Age in Britain no longer had to kill animals to make clothes, which meant that their lives really changed. Below is another example of a pupil drawing from their accumulated knowledge, in order to compare and contrast civilisations:

This is another example of a greater-depth learner in action. They had knowledge of Greece and Rome, and a battle that took place. Already, it is clear that they have an understanding of the cross-over and interaction between these two civilisations. Not only this, but they also know that trade took place between the two civilisations. Finally, they have commented on how this trade is clear from primary evidence. This pupil has not only demonstrated that they hold a secure knowledge of the Battle of Corinth, but they have also highlighted their ability to use evidence to draw their own historically valid conclusions.
To support and enable pupils to draw conclusions and analogies from historical sources, it is vital for the teacher to model how to do this (Runeckles, 2018:52). In mathematics, for example, you would not expect children to solve a worded problem on multiplication, which required reasoning, without first teaching them the basic skills of multiplication. How often do you model being a historian to your class?
For example, imagine you are teaching your class about the Spartans. The written sources on Sparta derive largely from sources written at a much later date, and not composed by Spartans. One could take an example from a Roman scholar (Aristotle or Plato) on the Spartan education system, the Agoge, and explain that these individuals were Roman and lived two hundred years after Classical Greece had ended. One could then ask, “How might that affect their account?” This sort of task could be implemented within a range of topics and encourages a dialogue between teachers and pupils. If these enquiry-based examples and questions are built into lessons, across modules, pupils are provided with opportunities to enhance their ability to analyse evidence and draw conclusions from a vast amount of evidence.
And finally…
Although I have separated the teaching of history into historical knowledge, historical understanding and historical enquiry, ultimately each of these elements is best taught concurrently. It is possible to include each of these aspects within one lesson, particularly as they are inextricably linked.
Perhaps most importantly, it is crucial to ensure that teachers are ambitious, not only with curriculum coverage, but also with regards to their expectations of pupils. Regardless of whether pupils have demonstrated that they are more able, children of all abilities thrive on high expectations and on knowing their teacher believes they can and will accomplish great things. So get your young historians thinking!
References
Read more:
Tags:
critical thinking
enquiry
history
humanities
KS2
literacy
problem-solving
questioning
Permalink
| Comments (0)
|
  
|
Posted By Emma Sanderson,
12 January 2021
|
Emma Sanderson, Head of English at NACE member and Challenge Award-accredited Hartland International School (Dubai), shares advice for successful use of “Genius Hour” project-based learning to challenge and motivate learners, inspired by Google’s “20% time”.
As teachers, our awareness of the importance of challenging questions is always at the forefront of our minds, particularly with our more able learners. However, the onus of asking challenging questions shouldn’t always be placed on the teacher. Cue Genius Hour, an idea inspired by Google’s “20% time”, in which employees are encouraged to spend 20% of their time working on any project of their choosing, on the condition that it ultimately benefits the company in some way, and which is famously credited with giving rise to many of Google’s most successful innovations.
Google’s “20% time” is similar to the use of Genius Hour in our school: encouraging students to take ownership of their learning by using a proportion of curriculum time to focus on topics they are passionate about. By coming up with their own driving question to focus their research, students manage their own learning journey and subsequently become even more engaged with the learning process.
Here are three key steps to use Genius Hour project-based learning effectively:
1) Support students to develop their driving question.
The driving question of the project will become the focus of the students’ research. Whilst students may be tempted to simply find out more information about a topic close to their heart, the key is to construct a question that allows for in-depth research and is also broad enough for students to include their personal opinions. Even our most able learners will need support with this task, and for this, question stems can be incredibly useful:
- What does _______ reveal about _________?
- To what extent does…?
- What motivates_________?
- How would you develop…?
- What alternatives are there for…?
- How can technology be used to…?
- What assumptions are there about…?
- What are the [ethical] implications of…?
- How can we challenge…?
- What would happen if…?
- How can we improve…?
- What might happen if…?
Students might be encouraged to come up with solutions to real-life problems or delve into ideas linked to current affairs that they are intrigued by. Either way, these broad question stems allow for thorough exploration of a topic.
2) Help students develop their research skills.
Left to their own devices, students may be tempted to simply Google their question and see what answers come up. Instead, offer guidance on the best and most reliable sources of information for their project.
It may be that students are directed towards relevant reference books in the library. Additionally, online resources can prove invaluable; the Encyclopaedia Britannica offers a wealth of knowledge for students, whilst news websites aimed at teenagers (for example Newsela and The Day) encourage students to form their own opinions on current affairs and offer suggestions for further reading.
Our more able learners may be more adept at focusing their internet searches and filtering through the vast array of results. If this is the case, students would be expected to determine whether a source is reliable or biased and should be confident at citing their sources.
3) Encourage creativity in how students present their findings.
Ideally, students will be excited and motivated to complete their Genius Hour project, and originality in how they present their results should be encouraged. Students may want to create a video, make a presentation, write a passionate and persuasive speech, design an informative leaflet… The more freedom the students have, the more their creativity will flourish.
One of our students gave a rousing speech on the question, “What alternatives are there to living on planet Earth?” (ultimately concluding there were none and that we need to change our lifestyles in order to save the planet). Another offered a passionate presentation on the theme “How can we improve Earth’s biodiversity while allowing people to still eat meat and plants?” And after witnessing the impact of Covid-19 first hand, one student wrote an insightful article to answer the question, “What has Covid-19 revealed about our society in 2020?”
This approach to project-based learning can also be effectively applied during distance learning – students can be given the success criteria for the project and set the challenge of managing their own time. There is ample opportunity to use technology to give presentations remotely, either live through Zoom or Teams, or recorded individually using a platform such as Flipgrid.
In summary…
Overall, Genius Hour is a fantastic tool to promote deeper thinking in the classroom, whilst also having huge benefits across the wider curriculum. We have found this approach has worked particularly well with Key Stage 3 students and is the perfect opportunity to refine the research and presentation skills required at GCSE, whilst also impacting positively across the curriculum in all lessons. Furthermore, it sends the message to students that their passions outside of school are valued, which in itself can prove to be hugely motivational. Presenting their findings at the end of the project instils confidence in our learners, giving them the vital communication, leadership and time management skills necessary for life beyond education.
Further reading: “Cognitive challenge: principles into practice”
NACE’s report “Cognitive challenge: principles into practice” explores approaches to curriculum and pedagogy which optimise the engagement, learning and achievement of very able young people, combining relevant research and theory with examples of current practice in NACE Challenge Award-accredited schools. Preview and order here.
Not yet a NACE member? Find out more, and join our mailing list for free updates and free sample resources.
Tags:
confidence
creativity
enquiry
enrichment
independent learning
motivation
problem-solving
project-based learning
questioning
research
Permalink
| Comments (0)
|
  
|
Posted By Ben Weddell, National Maritime Museum,
03 January 2018
Updated: 08 April 2019
|
The National Maritime Museum recently hosted a NACE member meetup exploring approaches to working in depth for the more able. Following on from the event, the museum’s Ben Weddell explains how an enquiry-based approach to history can be used to inspire and challenge learners of all ages and abilities.
Recently the National Maritime Museum (NMM) learning team were lucky enough to host a NACE member meetup. Following a presentation on SOLO Taxonomy and a “speed sharing” session, we had the opportunity to share the museum’s approach to teaching historical enquiry and how this can translate to the classroom, based on my experiences at the NMM and as a secondary history teacher.
History as an investigative process
A fascinating aspect of learning about the past is the realisation that we have to discover it. Far from a list of dates and occurrences to be memorised and regurgitated, history can – should – be an investigative subject of discovery.
This is a far more interesting and engaging approach, and one which provides opportunities to personalise and differentiate, by giving learners agency for the routes they take in uncovering the past.
Indeed, for history to have any meaning as a subject I would argue that it has to be investigative. It is through the skills which constitute a historical methodology that “history” comes to make sense as a coherent single subject.
Defining a historical method
If challenged about the scientific method, most teachers would be able to outline the “hypothesis, experimentation, new hypothesis” model. Is it possible to repeat that for history? If there is a scientific method that learners can grasp, surely there has to be an equivalent for history.
Historical enquiry is the skill that fills this gap. This starts from the premise that we don’t know what happened in the past and have to discover this for ourselves – a great learning opportunity as this is where learners themselves begin. Rather than treating learners as passive vessels to be topped up with historical information, this approach challenges them to uncover the past themselves.
Furthermore, there is an expectation in the national curriculum that enquiry will be taught:
“Pupils are expected to understand the methods of historical enquiry, including how evidence is used rigorously to make historical claims, and discern how and why contrasting arguments and interpretations of the past have been constructed.”
This process builds from KS1 to KS2 and 3, developing skills in dealing with isolated blocks of evidence and then establishing links between these, culminating in the ability to assess, ask questions of, and reflect on a large bank of potentially contradictory evidence and come to sound conclusions.
Harnessing the power of objects
One way to engage learners in this journey is to incorporate object-based enquiry. History teaching often focuses around the spoken and written word, resulting in a teacher-led approach. Using objects, especially in a multisensory capacity, can add interesting new dimensions to learning:
Increased motivation and curiosity
- Accessibility, through the ability for learners to raise their own questions
- Multisensory approaches providing different access points for a range of learners
- “Realness” – aiding understanding of abstract ideas through a focus on tangible objects
- Cross-curricular opportunities for literacy, incorporation of other forms of evidence and other subject areas
It is possible to build enquiry opportunities using a huge range of objects, so developing a specific object bank is useful but not essential. Whether making use of printed resources or actual physical objects, the process of conducting an enquiry is what brings the object to life.
Let learners find their own challenge
Larger enquiries offer extensive opportunities for teachers. The key is to provide a limited amount of initial evidence and then allow learners to formulate their own responses. This creates effective differentiation and provides unique opportunities for learners to create their own working level, including the more able.
Furthermore, a creative introduction to the initial information – say roleplaying an archaeological discovery or a new finding in a document or database – provides motivation for learners to set themselves a challenging question.
It is then possible to expand investigations with the introduction of new evidence. There is flexibility in the range and scope of evidence you introduce, which will be determined by learners’ needs and level. For instance, a limited suitcase of objects could be investigated by KS1 learners, whereas by KS3 a teacher could overload learners with objects, so they have to differentiate between useful evidence and red herrings or irrelevant information.
In practice this could take the form of:
- One-off mysteries (KS1/KS2): a collection of objects to consider and a simple guided outcome, for instance “Whose suitcase might this be?”
- Developed enquiries (KS2/KS3): building on initial discoveries to develop an entire scheme of work, for instance “Why was this object found in the Arctic?”, leading into a wider investigation of John Franklin’s doomed final voyage to the Arctic, linking more widely to Arctic exploration.
- Self-led enquiries (KS3): initial collection of evidence and a problem, leading to a project including opportunities for learners to define their own questions and route, selecting appropriate evidence from a wide range and engaging with controversies.
All of these models follow the same process – starting with initial evidence, developing a hypothesis, testing with additional evidence, then repeating with a new hypothesis and so on. The cyclical nature of this process is marked by increasing degrees of certainty in learners’ findings as they increase the depth and range of the evidence they have based their ideas upon.
Enquiry as part of a wider pedagogy
Making enquiry a central part of learning has a number of benefits. It revolves around approaching topics with a focus on teaching skills that can then be used to access content, as opposed to a discrete delivery of content and skills. In turn, this means that history begins to make coherent sense, challenging some learners’ misconception that it is “just stuff that has happened”.
The skills acquired will also be more easily transferable and encourage a cross-curricular approach. Significantly, these skills are highly applicable to a wider world in which the ability to assess and sift incoming information is becoming ever more crucial.
Historical enquiry fits well with other pedagogies, such as SOLO Taxonomy or other progressive models such as Bloom’s. As the enquiry progresses, individual learners move through different stages of thinking skills, with initial stages of identification and definition, progressing to description of evidence, classification and analysis, through to evaluation and hypothesising around a wide range of evidence.
This approach forms the basis for historical enquiry sessions at the National Maritime Museum. These sessions include KS1 investigations into where breakfast comes from, full-day secondary study sessions incorporating original archive materials, and expert research sessions for post-16 students. You can find out more about these sessions on our website or through our guide to school programmes, which can be found here.
Useful links:
- National Maritime Museum for schools – including information about school visits, CPD opportunities, downloadable resources and more.
- Royal Museums Greenwich collections – searchable database of the Royal Musuems Greenwich collections, ranging from maps and charts to a taxidermy penguin! Includes images and information which can easily be adapted as resources for teaching and learning.
- Spartacus Educational – free-to-use site hosting historical resources and materials, useful for creating banks of evidence to build an enquiry.
- Thinking History – website of Ian Dawson, one of the founders of the Schools History Project, with a huge array of fantastic enquiry-based sessions available for free.
Ben is a learning producer at the National Maritime Museum, Greenwich, where he specialises in historical enquiry programmes for learners of all ages. He previously worked as a history teacher in secondary schools and a sixth form college, with a particular interest in opportunities to build historical enquiry into the curriculum. To find out more about Ben’s work and how your school could get involved, contact NACE and we will put you in touch.
Tags:
enquiry
free resources
history
pedagogy
Permalink
| Comments (0)
|
|