Guidance, ideas and examples to support schools in developing their curriculum, pedagogy, enrichment and support for more able learners, within a whole-school context of cognitively challenging learning for all. Includes ideas to support curriculum development, and practical examples, resources and ideas to try in the classroom. Popular topics include: curriculum development, enrichment, independent learning, questioning, oracy, resilience, aspirations, assessment, feedback, metacognition, and critical thinking.
Top tags:
pedagogy
questioning
enrichment
research
curriculum
oracy
independent learning
aspirations
cognitive challenge
free resources
KS3
KS4
language
critical thinking
assessment
English
literacy
feedback
metacognition
resilience
collaboration
maths
confidence
creativity
vocabulary
wellbeing
access
lockdown
mindset
problem-solving
  
|
Posted By Bob Cox,
17 June 2022
|
Bob Cox, author of the Opening Doors books, reflects on the importance of high-quality, challenging texts for all pupils, and key factors for the successful implementation of a challenging English curriculum.
As the author of the Opening Doors series of books for English at KS1, 2 and 3, I’ve had the pleasure of developing a UK-wide network of schools and organisations committed to providing an enriched diet of English where every pupil has the opportunity to relish new challenges. This is particularly pertinent for those advanced pupils whose whole morale can be threatened by revisiting concepts they have already mastered; but it is just as vital for pupils whose reading scores may be low.
We are seeing the high-pitch approaches, encouraged by so many educationists, being turned into reality in the day-to-day classroom by teachers using top-quality texts, poetry, quirky short extracts and contemporary children’s literature with a ‘meaty’ depth. The sheer scope of the language and style is a springboard to genuine comprehension journeys with the teacher’s questioning, knowledge transmission and fascinating oracy being delivered through an inspiring range of methodology. Such is the scope for learning in challenging texts, that the knowledge acquired in the reading can then be applied to the writing.
For example, just read a few lines of Dionne Brand’s Wind:
I pulled a hummingbird out of the sky one day
but let it go
I heard a song and carried it with me
On my cotton streamers
I dropped it on an ocean and lifted up a wave
With my bare hands…
Now see what Faith Gorman, a pupil at Red Barn Primary, has written:
I came in the night,
Luminous black,
Dashing, darting,
I made the street lamps flicker and jerk as I swept by,
I saw the foxes and owls capture their prey…
You can well imagine the range of teaching methodology, word power building and drafting that will have gone on in the process, but without Dionne Brand’s image-making and without overtly exploring the language and techniques, the crafting of the writing would have been less imaginative. There would also have been less knowledge about language acquired: personification, rhythm and meaning; specific vocabulary choices.
Using complex texts and developing the teaching strategies to go with them is key: “start kids out with complex texts that they cannot read successfully; then teach them to read those texts well.” – Timothy Shanahan, February 2017
In my work many years ago as an LA consultant and a freelance deliverer of provision for able pupils – then called ‘gifted and talented’ – there was huge interest from schools in the potential behind the devising of a top-class curriculum; but there were huge concerns about pupils with low reading scores being left behind. That made a lot of sense. In addition, there were concerns that pupils with high learning potential actually disliked risk-taking so much that moving them on to high-level texts and questions was not easy. Schools still report that pupils with very high potential can get upset about an incorrect answer, whereas other pupils can be so used to difficulties that they find it normal to ask their way out of them. [For more on this, take a look at NACE’s work on perfectionism in partnership with York St John University.]
Clearly, challenge for every pupil must become a habit, a norm, an expectation – and then the pupils demand it themselves instead of being wary! I’ve seen this happen in many schools. Resilience grows and healthy ambition prospers. Getting unstuck becomes fascinating, not threatening.
So, when I came to write books for English, pitched high, often asking more of pupils in terms of depth of thinking and breadth of quality reading, I was determined to ensure inclusive routes to excellence which would support equality of opportunity and social justice, and recognising the entitlement to high-class literature – from past to present and across the globe – for all learners, but pitched beyond where the most advanced pupil might be.
These are some key ways in which we have supported schools which are following the Opening Doors approach, and schools have fed back to us as a community growing in knowledge together.
So, what allows those doors to open?
- A whole-school action plan is needed to design an English curriculum which progresses from challenge to challenge, concept to concept, and through transition into KS3.
- Access strategies should flow through the curriculum: scaffolding, responding to need, clarifying, exemplifying and adapting. Pitch high but offer support when needed.
- See the sample units under free resources on my website for examples of our radial questioning layouts, which end the notion of very able pupils treading water on easy questions. We move them straight to high-level challenges if they are ready.
- Opening Doors schools build in whole-text reading in rich and immersive ways, with plenty of choice. Alongside this, extracts provide a focus for language study, depth and comprehension explorations; link reading provides range and diversity in an ethos of skilled facilitation and expectation.
- Teachers develop their own reading and expertise, offering that to pupils as the most wonderful opening of doors to general knowledge, increased confidence and articulation of ideas that there can be.
So, the quality of the text explored deepens learning immeasurably, and that new learning is applied in ambitious writing – but it’s the teacher who makes the difference! Without you, it’s much harder for this to happen.
Reference
Brand, Dionne (2006; originally published 1979), Earth Magic. Toronto: Kids Can Press Ltd.
Full unit features in: Cox, Bob (2019), Opening Doors to a Richer English Curriculum, ages 6-9. Carmarthenshire: Crown House.
Find out more…
To learn more about the Opening Doors approach, explore Bob Cox’s website. Plus: Bob online on 13 October 2022 for an exclusive live webinar for NACE members – register here.
If you would like to buy the Opening Doors books for your school, remember that NACE members can currently benefit from a 20% discount on all purchases from the Crown House Publishing website. For details of this and all current member discounts, visit our member offers page (login required).
Tags:
cognitive challenge
curriculum
depth
English
KS1
KS2
language
literacy
literature
pedagogy
perfectionism
questioning
reading
transition
vocabulary
writing
Permalink
| Comments (0)
|
  
|
Posted By Tom Stewart,
01 April 2022
|
Tom Stewart, Head of History at Maiden Erlegh School, sets out tangible strategies that he and his department take when challenging more able students in history lessons.
History at secondary school level is a subject that, from my experience, is usually taught in mixed ability classes. Due to this, and to rightfully ensure the progress of those who struggle with literacy and require further support, lessons can tend to be pitched towards the middle with scaffolding and structure in place to help those struggling. The potential problem with this approach is that it risks neglecting the more able students and those who need to be challenged or stretched (or whichever phrase is used in your setting), to reach their potential. I hope this blog post will give you some ideas to take away to challenge the more able learners in your history lessons.
#1. Short-term: Questioning
A simple and easy way to challenge those more able students is through effective use of the questioning they face in a lesson. I imagine most teachers know about open and closed questions and how the latter can limit students to a one-word answer, whilst the former can require students to elaborate in more depth. Therefore, the answer the students give can often depend on how much thought has gone into the question asked.
It is important to consider why a teacher is asking a question and this can then be applied to challenging the more able students by asking a variety of questions for different reasons. In a recent CPD session at my school, delivered by two excellent Assistant Headteachers, Rob Buck and Ben Garner, this principle, with some examples, was shared with staff (Figure 1). It reminded myself and my department to think carefully about the questioning we carried out and to target those more able students, whether they be in Year 7, Year 10 or Year 13.
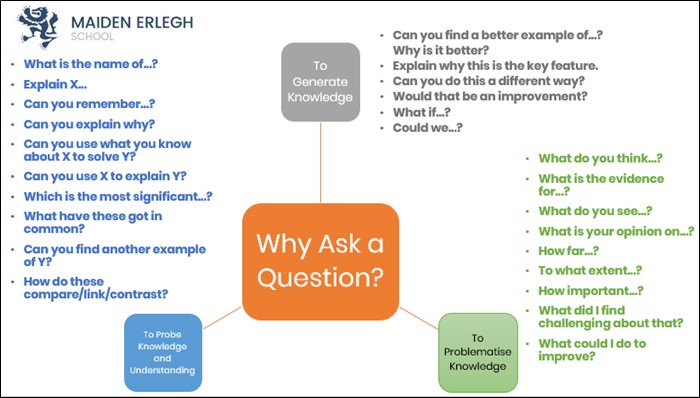
Figure 1
#2. Medium-term: Widen their perspectives
More able students are often characterised by a curious and inquisitive nature. To support this, it is important to not be overly selective with the history shared with students, but find opportunities to reveal more of the story. Students of all abilities enjoy learning knowledge that isn’t necessarily vital to the topic – knowledge that Bailey-Watson calls ‘hinterland’ knowledge – and we should be willing to share with students more of the big picture in order to widen their perspectives and improve their historical thinking.
Homework can be an outlet for this; the previously mentioned Bailey-Watson and Kennet launched their ‘meanwhile, elsewhere…’ project (Figure 2) with the explicit intention of ‘expanding historical horizons’. Used effectively, this is a strategy that challenges the more able students to make those links between what they know and what they are yet to know.

Figure 2
#3. Long-term: Enquiry-based topics
History lends itself to a wealth of interesting topics. This selection narrows at GCSE and A-Level as specifications force middle leaders to select one topic and not another. However, at Key Stage 3, there is normally more choice and also an opportunity to challenge more able students. We have found evolving already-established topics – or creating new ones where time allowed and necessity demanded – into enquiry-based ones supports more able students by forcing them to ‘think hard’.
Our topic on the Norman Conquest, an event described by Peter Rex as ‘the single most important event in English history’ avoids a simpler narrative of events and instead forces students, especially the more able, to consider how King William managed not only to gain control but maintain it after the Battle of Hastings (Figure 3). This topic was designed by my fantastic colleague, Chloe Bateman, and this approach provides all students with an overview of where the lesson and topic fits in and also encourages deep thinking about the answer to the enquiry question before it has even been covered.
Combined with sharing demanding texts with students in lessons and homework that relates directly to the enquiry question, whilst extending their knowledge and understanding even further, enquiry-based topics can prove very effective at challenging more able students in secondary history.
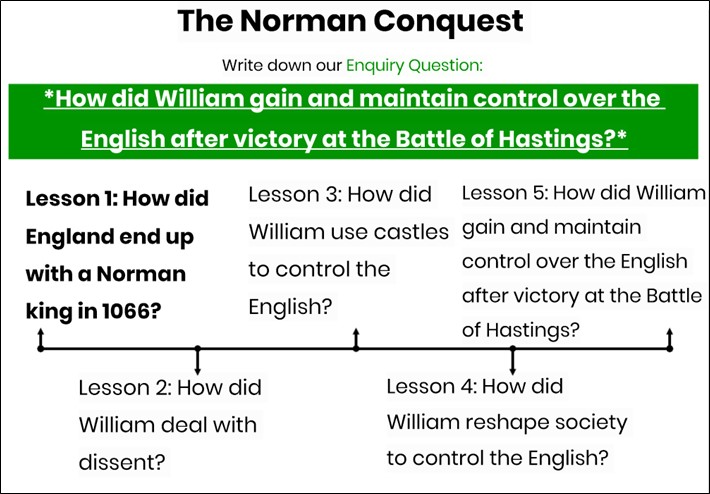
Figure 3
There are plenty of strategies out there and there are more that I use and could have shared with you, but here are three that you could look to introduce to your setting. The important point is to be mindful about the experience more able students get in our classrooms. Do they feel challenged? Would you in their shoes? If not, then be active in doing something about it.
References
- Bailey-Watson, W. and Kennett, R. (2019). '"Meanwhile, elsewhere…": Harnessing the power of community to expand students’ historical horizons’, Teaching History, 176.
- https://meanwhileelsewhereinhistory.wordpress.com/
- Paramore, J. (2017). Questioning to Stimulate Dialogue, in Paige R., Lambert, S. and Geeson, R. (eds), Building Skills for Effective Primary Teaching, London: Learning Matters.
- Rex, P. (2011). 1066: A New History of the Norman Conquest, Amberley Publishing.
Read more:
Tags:
enquiry
history
humanities
KS3
KS4
KS5
questioning
Permalink
| Comments (0)
|
  
|
Posted By Daisy Morley,
28 March 2022
Updated: 22 March 2022
|
Daisy Morley, primary teacher and history lead at Calcot Schools, outlines her approach to identifying and challenging more able learners in history – building historical knowledge, understanding and enquiry skills.
As a teacher it currently seems to me that a lot of attention is given to the children who need to meet age-related expectations. While these pupils’ needs are important and their needs must be met, this focus can mean that greater depth and ‘more able’ pupils are often forgotten. It is essential that more able learners are not neglected and are given ample opportunities to showcase their knowledge and shine.
History is one subject where, through careful consideration and planning, more able learners can thrive. Within this blog post, I will examine how to identify and challenge more able learners in history, in the context of primary teaching. These thoughts derive from personal experiences and from extensive research on the relevant literature and recent Ofsted reports. I will focus on ‘historical knowledge’, ‘historical understanding’ and ‘historical enquiry’ in order to suggest how we can think about challenging more able learners in history.
More able in history or just literacy?
Often, children whose strength lies in history will find that they are confident in literacy. Although strong literacy skills will greatly benefit their ability to share, form and communicate their ideas and findings, this does not necessarily mean that they are or will be more able historians. Interestingly, I think that the personal interests of children play a pivotal part in whether they have excelled in history beyond their age-related expectations. This is true from children as young as Year 1, to pupils nearing the end of their primary education. As educators, particularly if you are a subject leader, it is essential that time is taken to identify those children with a personal interest in history, and to provide them with opportunities to showcase their knowledge.
The building blocks: historical knowledge
First and foremost, the subject of history is rooted in knowledge; it is a knowledge-based subject (Runeckles, 2018: 10). While it is essential that pupils’ analytical skills are developed, this cannot be done without first ensuring that all pupils have a secure grounding in historical knowledge. This is also made clear in recent literature from Ofsted inspectors. Tim Jenner, HMI, Ofsted’s subject lead for history, has stated that when teaching history there must be an emphasis placed on content and knowledge (Jenner, 2021). In the most recent Ofsted reports, the term ‘knowledge’ has been divided into knowledge of ‘substantive concepts’, which relates to broader concepts, such as empire, monarch and economy, and ‘chronological knowledge’, which refers to the broader concepts within history, such as the key features of Anglo-Saxon England (Jenner, 2021).
The National Curriculum does expect pupils to “understand the methods of historical enquiry, including how evidence is used rigorously to make historical claims, and discern how and why contrasting arguments and interpretations of the past have been constructed” (DFE, 2013). The enquiry and analytical skills required to thrive in history are essential. However, these skills cannot be developed without first imparting the key historical knowledge to children.
Facts are the building blocks of history.
To emphasise this point, let us look at an example. Imagine a teacher wants to include a module on Boudicca in their history curriculum. Boudicca is listed in the National Curriculum for History under a non-statuary example, and has crucial ties with the statuary module on the Roman Empire and its impact on Britain. For the pupils to understand Boudicca’s historical significance, they would first need to have a secure grasp of the key features of the Roman Empire. Following this, they would then need to be taught the key components of Britain during this time. This knowledge would be essential before embarking on a specialised study of Boudicca. If the teacher then wished to hone and develop pupils’ analytical and enquiry skills, they could include a lesson on the conflicting sources that are available regarding Boudicca. To understand the primary written sources, however, they would first need to have a secure understanding of the historical knowledge of Boudicca, the Roman Empire, and the political landscape of Britain during this time.
Building historical knowledge takes time, as it requires a build-up of knowledge. As a result, educators may not see this accumulation of knowledge until a significant period of learning time has passed. Nevertheless, for children to develop their enquiry skills, historical knowledge is essential.
Developing historical understanding through open-ended questions
To see progression within a pupil’s historical understanding, historical knowledge, understanding and enquiry are best taught alongside one another. Historical knowledge and understanding are inextricably linked, and it would be difficult to separate these concepts within every lesson. Nevertheless, if a child is demonstrating the potential to achieve beyond the age-related expectations in history, their historical understanding could be one way to identify this – and thus to extend and challenge their learning. More able learners often process the key historical knowledge more quickly than their peers, which in turn means that they often quickly grasp the role of criteria in formulating and articulating an historical explanation or argument. Furthermore, more able learners are frequently able to draw generalisations and conclusions from a range of sources of evidence. One way to identify this could be ensuring that teachers ask open-ended questions, as the answers that children arrive at depend largely on questions asked.
I try to implement these open-ended questions in lessons, particularly across Key Stage 2. One approach which has worked particularly well came to light in a Year 3 lesson on “What did the diet of a typical Stone Age person encompass in prehistoric Britain?” This lesson relied on enquiry-based learning, which, although sometimes more difficult to deliver, lent itself well to inputting open-ended questions and highlighted the investigative nature of history. The children were given ‘organic evidence’ (pretend human waste), which pivoted around unpicking evidence and how historians use different types of evidence to find out about the past.
From this lesson, after unpicking our evidence, all of the children were able to deduce that prehistoric people ate nuts, seeds and berries. Pupils with a more advanced understanding were able to conclude that prehistoric inhabitants had to find food for themselves and that this is one of the reasons people from that time are called ‘hunter-gatherers’, because they had to hunt and gather their food.
For the children who had already come to the conclusions about hunter-gatherers, I asked more open-ended questions, which required them to draw their own conclusions, using the evidence that had been assessed, including “What about the meat?”, “Why haven’t we found meat in the organic evidence?” Some of these children were able to utilise their knowledge from previous lessons on Stone Age Britain and concluded that there were certain dangers in finding meat. They explained that people had to kill the animal and prepare it themselves, which was dangerous. One child even went on to say that meat also rots and that may have been why there was no surviving meat within the evidence. Although these open-ended questions help to stretch the more able learners, it does require teachers to direct the more challenging questions to the correct pupils, which relies on teachers knowing which of the pupils are excelling in history.
Making links: developing historical enquiry skills
I often find that historical enquiry skills are the hardest to master. From teaching this within lessons, it seems the key component to identifying the more able learners in history is to identify whether the pupils can link history together. Can they use their knowledge to comment on how the lives of people from the past have changed over time? Can they identify trends and commonalities between contemporary cultures? Do they notice how key changes transformed the lives and the culture of a particular civilisation? Perhaps most essentially, can the more able children use their historical knowledge and understanding to draw conclusions on events, people and places from the past? This relies on a pupil being able to problem-solve and reason with evidence, and apply this knowledge in order to evaluate the evidence in question.
Below is an example of a child’s work. The lesson was titled “What was bronze used for?”

I have chosen this example because this pupil was able to link their knowledge together, to form their own conclusions, which were based on key factual knowledge. For example, this child independently came to the conclusion that because their weapons were better, their quality of life improved. Amazingly, this pupil also commented on the fact that people from the Bronze Age in Britain no longer had to kill animals to make clothes, which meant that their lives really changed. Below is another example of a pupil drawing from their accumulated knowledge, in order to compare and contrast civilisations:

This is another example of a greater-depth learner in action. They had knowledge of Greece and Rome, and a battle that took place. Already, it is clear that they have an understanding of the cross-over and interaction between these two civilisations. Not only this, but they also know that trade took place between the two civilisations. Finally, they have commented on how this trade is clear from primary evidence. This pupil has not only demonstrated that they hold a secure knowledge of the Battle of Corinth, but they have also highlighted their ability to use evidence to draw their own historically valid conclusions.
To support and enable pupils to draw conclusions and analogies from historical sources, it is vital for the teacher to model how to do this (Runeckles, 2018:52). In mathematics, for example, you would not expect children to solve a worded problem on multiplication, which required reasoning, without first teaching them the basic skills of multiplication. How often do you model being a historian to your class?
For example, imagine you are teaching your class about the Spartans. The written sources on Sparta derive largely from sources written at a much later date, and not composed by Spartans. One could take an example from a Roman scholar (Aristotle or Plato) on the Spartan education system, the Agoge, and explain that these individuals were Roman and lived two hundred years after Classical Greece had ended. One could then ask, “How might that affect their account?” This sort of task could be implemented within a range of topics and encourages a dialogue between teachers and pupils. If these enquiry-based examples and questions are built into lessons, across modules, pupils are provided with opportunities to enhance their ability to analyse evidence and draw conclusions from a vast amount of evidence.
And finally…
Although I have separated the teaching of history into historical knowledge, historical understanding and historical enquiry, ultimately each of these elements is best taught concurrently. It is possible to include each of these aspects within one lesson, particularly as they are inextricably linked.
Perhaps most importantly, it is crucial to ensure that teachers are ambitious, not only with curriculum coverage, but also with regards to their expectations of pupils. Regardless of whether pupils have demonstrated that they are more able, children of all abilities thrive on high expectations and on knowing their teacher believes they can and will accomplish great things. So get your young historians thinking!
References
Read more:
Tags:
critical thinking
enquiry
history
humanities
KS2
literacy
problem-solving
questioning
Permalink
| Comments (0)
|
  
|
Posted By Elena Stevens,
28 March 2022
Updated: 24 March 2022
|
History lead and author Elena Stevens shares four approaches she’s found to be effective in diversifying the history curriculum – helping to enrich students’ knowledge, develop understanding and embed challenge.
Recent political and cultural events have highlighted the importance of presenting our students with the most diverse, representative history curriculum possible. The murder of George Floyd in May 2020 and the tearing down of Edward Colston’s statue the following month prompted discussion amongst teachers about the ways in which we might challenge received histories of empire, slavery and ‘race’; developments in the #MeToo movement – as well as instances of horrific violence towards women – have caused many to reflect on the problematic ways in which issues of gender are present within the curriculum. Diversification, decolonisation… these are important aims, the outcomes of which will enrich the learning experiences of all students, but how can we exploit the opportunities that they offer to challenge the most able?
At its heart, a more diverse, representative curriculum is much better placed to engage, inspire and include than one which is rooted in traditional topics and approaches. A 2018 report by the Royal Historical Society found that BAME student engagement was likely to be fostered through a broader and more ‘global’ approach to history teaching, whilst a 2014 study by Mohamud and Whitburn reported on the benefits of – in Mohamud and Whitburn’s case – shifting the focus to include the histories of Somali communities within their school. A history curriculum that reflects Black, Asian and ethnic minorities, as well as the experiences of women, the working classes and LGBT+ communities, is well-placed to capture the interest and imagination of young people in Britain today, addressing historical and cultural silences. There are other benefits, too: a more diverse offering can help not only to enrich students’ knowledge, but to develop their understanding of the historical discipline – thereby embedding a higher level of challenge within the history curriculum.
Below are four of the ways in which I have worked to diversify the history schemes of work that I have planned and taught at Key Stages 3, 4 and 5 – along with some of the benefits of adopting the approaches suggested.
1: Teach familiar topics through unfamiliar lenses
Traditionally, historical conflicts are taught through the prism of political or military history: students learn about the long-term, short-term and ‘trigger’ causes of the conflict; they examine key ‘turning points’; and they map the war’s impact on international power dynamics. However, using a social history approach to deliver a scheme of work about, for example, the English Civil War, complicates students’ understanding of the ‘domains’ of history, shifting the focus so that students come to appreciate the numerous ways in which conflict impacts on the lives of ‘ordinary’ people. The story of Elizabeth Alkin – the Civil War-era nurse and Parliamentary-supporting spy – can help to do this, exposing the shortfalls of traditional disciplinary approaches.
2: Complicate and collapse traditional notions of ‘power’
Exam specifications (and school curriculum plans) are peppered with influential monarchs, politicians and revolutionaries, but we need to help students engage with different kinds of ‘power’ – and, beyond this, to understand the value of exploring narratives about the supposedly powerless. There were, of course, plenty of powerful individuals at the Tudor court, but the stories of people like Amy Dudley – neglected wife of Robert Dudley, one of Elizabeth I’s ‘favourites’ – help pupils gain new insight into the period. Asking students to ‘imaginatively reconstruct’ these individuals’ lives had they not been subsumed by the wills of others is a productive exercise. Counterfactual history requires students to engage their creativity; it also helps them conceive of history in a less deterministic way, focusing less on what did happen, and more on what real people in the past hoped, feared and dreamed might happen (which is much more interesting).
3: Make room for heroes, anti-heroes and those in between
It is important to give the disenfranchised a voice, lingering on moments of potential genius or insight that were overlooked during the individuals’ own lifetimes. However, a balanced curriculum should also feature the stories of the less straightforwardly ‘heroic’. Nazi propagandist Gertrud Scholtz-Klink had some rather warped values, but her story is worth telling because it illuminates aspects of life in Nazi Germany that can sometimes be overlooked: Scholtz-Klink was enthralled by Hitler’s regime, and she was one of many ‘ordinary’ people who propagated Nazi ideals. Similarly, Mir Mast challenges traditional conceptions of the gallant imperial soldiers who fought on behalf of the Allies in the First World War, but his desertion to the German side can help to deepen students’ understanding of the global war and its far-reaching ramifications.
4: Underline the value of cultural history
Historians of gender, sexuality and culture have impacted significantly on academic history in recent years, and it is important that we reflect these developments in our curricula, broadening students’ history diet as much as possible. Framing enquiries around cultural history gives students new insight into the real, lived experiences of people in the past, as well as spotlighting events or time periods that might formerly have been overlooked. A focus, for example, on popular entertainment (through a study of the theatre, the music hall or the circus) helps students construct vivid ‘pictures’ of the past, as they develop their understanding of ‘ordinary’ people’s experiences, tastes and everyday concerns.
There is, I think, real potential in adopting a more diversified approach to curriculum planning as a vehicle for embedding challenge and stretching the most able students. When asking students to apply their new understanding of diverse histories, activities centred upon the second-order concept of significance help students to articulate the contributions (or potential contributions) that these individuals made. It can also be interesting to probe students further, posing more challenging, disciplinary-focused questions like ‘How can social/cultural history enrich our understanding of the past?’ and ‘What can stories of the powerless teach us about __?’. In this way, students are encouraged to view history as an active discipline, one which is constantly reinvigorated by new and exciting approaches to studying the past.
About the author
Elena Stevens is a secondary school teacher and the history lead in her department. Having completed her PhD in the same year that she qualified as a teacher, Elena loves drawing upon her doctoral research and continued love for the subject to shape new schemes of work and inspire students’ own passions for the past. Her new book 40 Ways to Diversify the History Curriculum: A practical handbook (Crown House Publishing) will be published in June 2022.
NACE members can benefit from a 20% discount on all purchases from the Crown House Publishing website; for details of this and all NACE member offers, log in and visit our member offers page.
References
Further reading
- Counsell, C. (2021). ‘History’, in Cuthbert, A.S. and Standish, A., eds., What should schools teach? (London: UCL Press), pp. 154-173.
- Dennis, N. (2021). ‘The stories we tell ourselves: History teaching, powerful knowledge and the importance of context’, in Chapman, A., Knowing history in schools: Powerful knowledge and the powers of knowledge (London: UCL Press), pp. 216-233.
- Lockyer, B. and Tazzymant, T. (2016). ‘“Victims of history”: Challenging students’ perceptions of women in history.’ Teaching History, 165: 8-15.
More from the NACE blog
Tags:
critical thinking
curriculum
history
humanities
KS3
KS4
KS5
questioning
Permalink
| Comments (0)
|
  
|
Posted By Kirstin Mulholland,
15 February 2022
|
Dr Kirstin Mulholland, Content Specialist for Mathematics at the Education Endowment Foundation (EEF), shares a metacognitive strategy she’s found particularly helpful in supporting – and challenging – the thinking of higher-attaining pupils: “the debrief”.
Why is metacognition important?
Research tells us that metacognition and self-regulated learning have the potential to significantly benefit pupils’ academic outcomes. The updated EEF Teaching and Learning Toolkit has compiled well over 200 school-based studies that reveal a positive average impact of around seven months progress. But it also recognises that "it can be difficult to realise this impact in practice as such methods require pupils to take greater responsibility for their learning and develop their understanding of what is required to succeed” .
Approaches to metacognition are often designed to give pupils a repertoire of strategies to choose from, and the skills to select the most suitable strategy for a given learning task. For high prior attaining pupils, this offers constructive and creative opportunities to further develop their knowledge and skills.
How can we develop metacognition in the classroom?
In my own classroom, a metacognitive strategy which I’ve found particularly helpful in supporting – and, crucially, challenging – the thinking of higher-attaining pupils is “the debrief”. The debrief as an effective learning strategy links to Recommendation 1 of the EEF’s Metacognition and Self-regulated Learning Guidance Report (2018), which highlights the importance of encouraging pupils to plan, monitor and evaluate their learning.
In a debrief, the role of the teacher is to support pupils to engage in “structured reflection”, using questioning to prompt learners to articulate their thinking, and to explicitly identify and evaluate the approaches used. These questions support and encourage pupils to reflect on the success of the strategies they used, consider how these could be used more effectively, and to identify other scenarios in which these could be useful.
Why does this matter for higher-attaining pupils?
When working in my own primary classroom, I found that encouraging higher-attaining pupils to explicitly consider their learning strategies in this way provides an additional challenge. Initially, many of the pupils I’ve worked with have been reluctant to slow down to consider the strategies they’ve used or “how they know”. Some have been overly focused on speed or always “getting things right” as an indication of success in learning.
When I first introduced the debrief into my own classroom, common responses from higher-attaining pupils were “I just knew” or “It was in my head”. However, what I also experienced was that, for some of these pupils, because they were used to quickly grasping new concepts as they were introduced, they didn’t always develop the strategies they needed for when learning was more challenging. This meant that, when faced with a task where they didn’t “just know”, some children lacked resilience or the strategies they needed to break into a problem and identify the steps needed to work through this.
As I incorporated the debrief more and more frequently into my lessons, I saw a significant shift. Through my questioning, I prompted children to reflect on the rationale underpinning the strategies they used. They were also able to hear the explanations given by others, developing their understanding of the range of options available to them. This helped to broaden their repertoire of knowledge and skills about how to be an effective learner.
How does the debrief work in practice?
Many of the questions we can use during the debrief prompt learners to reflect on the “what” and the “why” of the strategies they employed during a given task. For example,
- What exactly did you do? Why?
- What worked well? Why?
- What was challenging? Why?
- Is there a better way to…?
- What changes would you make to…? Why?
However, I also love asking pupils much more open questions such as “What have you learned about yourself and your learning?” The responses of the learners I work with have often astounded me! They have encompassed not just their understanding of the specific learning objectives identified for a given lesson, but also demonstrating pupils’ ability to make links across subjects and to prior learning. This has led to wider reflections about their metacognition – strengths or weaknesses specific to them, the tasks they encountered, or the strategies they had used – or their ability to effectively collaborate with others.
For me, the debrief provides an opportunity for pupils’ learning to really take flight. This is where reflections about learning move beyond the boundaries and limitations of a single lesson, and instead empower learners to consider the implications of this for their future learning.
For our higher-attaining pupils, this means enabling them to take increasing ownership over their learning, including how to do this ever more effectively. This independence and control is a vital step in becoming resilient, motivated and autonomous learners, which sets them up for even greater success in the future.
References
Tags:
cognitive challenge
critical thinking
language
maths
metacognition
pedagogy
problem-solving
questioning
Permalink
| Comments (0)
|
  
|
Posted By Ann McCarthy,
14 February 2022
|
Dr Ann McCarthy, NACE Research and Development Director
It may seem strange to find an article with both metacognition and assessment in the title. Many people still view assessment as an activity which is separate from the art of teaching and is simply a list of checks and balances required by the education system to set targets, track learning, report to stakeholders and finally to issues qualifications. However, for those who are using assessment routinely, and at all points within the act of teaching and learning, they know the power of assessment which is both explicit and implicit within the process. The drive to focus on metacognition, for all ages of pupils, has opened opportunities for assessment practices to be developed within the classroom both by the teacher and by the pupils themselves.
Contents:
The story so far: summative and formative assessment
Historically, assessment processes were strongly linked to the curriculum and planned content because they responded to an education system which prepared pupils for endpoint examinations. This approach is still evident within the many summative assessments, tests of memory or vocabulary and algorithmic routines seen in classrooms today. One can understand the reliance on these practices as they lead to the maintenance of a school’s grade profile and with good teaching and leadership can promote improvements in external measures. It feels safe!
The strength of this type of assessment is that it can provide baseline markers or diagnostic information. Here the assessment focus is always linked to the curriculum, the content and the examination. Good teaching can then move pupils closer to the end goal. When pupils respond well to this style, they can gain the required results – but too often pupils do not respond well and do not necessarily develop beyond the limits of the examination style question. Here the agenda is owned by the teacher, with pupils expected to respond to the demands of the model.
The weakness of this style of assessment is that there is little space for variation to reflect the personalities and learning styles of pupils or to allow more able pupils to learn beyond the examination. Here pupils are trained to meet the end goal without necessarily seeing the potential of the learning beyond the final grade. How often do we hear people say “I can’t do this” or “I don’t know this” although it may be a subject studied in school?
The development of formative assessment in different teaching contexts has increased teachers’ understanding of cognition and cognitive strategies alongside subject-specific skills and content. However, teachers can still be drawn into summative assessment practices in the guise of formative assessment. These are often recall or memory activities or small-scale versions of summative assessments aligned to endpoint assessment.
Good formative assessment is embedded in the planning for teaching and classroom practice. An understanding of the assessment measures and effective feedback will enable pupils to take some ownership of their learning. However, in a cognitively challenging learning environment we seek to empower pupils to own their learning and to become resilient, independent learners. So how then can we think differently about assessment practice?
Limitations to traditional formative and summative assessment practices
With traditional summative and formative assessment methods pupils are responsive to the demands and expectations of the teacher. They are expected to act in response to assessment outcomes and teacher feedback, using the methods and strategies modelled or directed by the teacher. The teacher plans the content, makes a judgement and creates opportunities to gain experience within the planned model. The teacher then assesses within this model and offers advice to the pupils about what they must do next and the actions which the teacher believes will lead to better learning and outcomes.
This can be successful in achieving the endpoint grades or examination standards. It does not necessarily develop pupils’ ability to do this for themselves, both within and beyond the education system.
Developing cognition and cognitive strategies
At the heart of good teaching and learning there is a focus on mental processes (cognition) and skills (cognitive strategies). The most effective classroom assessment makes use of cognition and the cognitive strategies beneficial to the specialist subject, which are most appropriate for the pupils.
The teacher of more able pupils aims to create cognitively challenging learning experiences, which must not be adversely affected by the assessments. This requires carefully selected strategies which hone the cognitive processes at the same time as developing subject expertise. Teaching builds from what pupils already know and understand, what they need to learn and what they have the potential to achieve. It develops the skills needed to apply knowledge, understanding and learning in a variety of contexts.
To maximise the impact of planned teaching on learning, effective assessment practices are essential. An important factor when planning for assessment, which goes beyond the confines of endpoint limitations, is that it places the pupil, rather than the content, at the centre of the process. Assessment activities should not simply measure current performance against a list of content-driven minimum standards, but also lead to a greater depth of knowledge and improved cognition. These assessments are not positioned separately from the learning but are at the heart of the learning and the development of cognitive strategies.
Assessments planned as part of – and not separate from – teaching and learning might include:
- High-quality classroom dialogic discourse;
- Big Questions;
- Teacher-pupil, pupil-teacher and pupil-pupil questioning;
- Collaborative pursuits aimed to generate new ideas;
- Adopting learning roles to enhance and extend current skills;
- Problem solving;
- Prioritisation tasks;
- Research;
- Investigations;
- Explaining and justifying responses;
- Analytical tasks;
- Examining misconceptions;
- Recall for facts in novel contexts;
- Organisation of knowledge to develop new ideas.
By examining learning in the moment, with pupils working independently or together on pre-planned tasks, with clear and measurable success criteria, the teacher can assess more accurately. Using the planned teaching and learning repertoire as the assessment, the teacher makes learning visible. The teacher will gain a greater understanding of the teaching models which lead to greater improvements in cognition. The teacher is then also able to establish which cognitive strategies are used most effectively and which need to be developed.
By maintaining the learning while assessing the teacher acts as a resource and a learning activator. Timely questions, redirecting actions or thoughts and providing feedback are among the variety of actions which can take place in the instant. This does not prevent an analysis of the level of knowledge or understanding of the subject. By working in this way, the teacher can provide more precise input to either the individual or the class; in the moment, it will have the greatest benefit.
In classrooms where the teacher combines their subject knowledge with their understanding of cognition, they will inevitably understand the nature and power of appropriate assessment. Teaching and assessment which is rooted in an understanding of cognition has the potential to prepare pupils for learning both within and beyond the classroom.
When the nature of the learning, the tasks and the assessments are shared with the pupils, they can begin to take ownership of their learning and develop their skills under the guidance of the teacher. Assessing through an understanding of cognition and cognitive strategies allows the teacher to share more fully the process of learning both in terms of academic outcomes but also in relation to thought and cognitive strategies. The pupils can now more fully impact on their own learning, but there is still a dependency on the teacher’s feedback and planning.
Once we appreciate the power of cognitively aware teaching, learning and assessment then we realise that pupils can take action to improve their thinking and learning if they know more. Metacognition means that pupils have a critical awareness of their own thinking and learning. They can visualise themselves as thinkers and learners. If the assessment, teaching and learning model moves the learner towards owning the learning, understanding their own cognition and cognitive strategies, then greater short-term and long-term gains can be made. Developing metacognitively focused classrooms will lead to a better quality of assessment which pupils will understand and can interrogate to refine their own learning.
When teachers look to develop metacognition as a whole-school strategy and within individual subject teaching there can be greater gains. The pupils will learn about the process of learning and come to understand ways in which they can best improve their own learning. Metacognition is about the ways learners monitor and purposefully direct their learning. If pupils develop metacognitive strategies, they can use these to monitor or control cognition, checking their effectiveness and choosing the most appropriate strategy to solve problems.
When planning teaching which makes use of metacognitive processes the teacher must first help pupils to develop specific areas of knowledge.
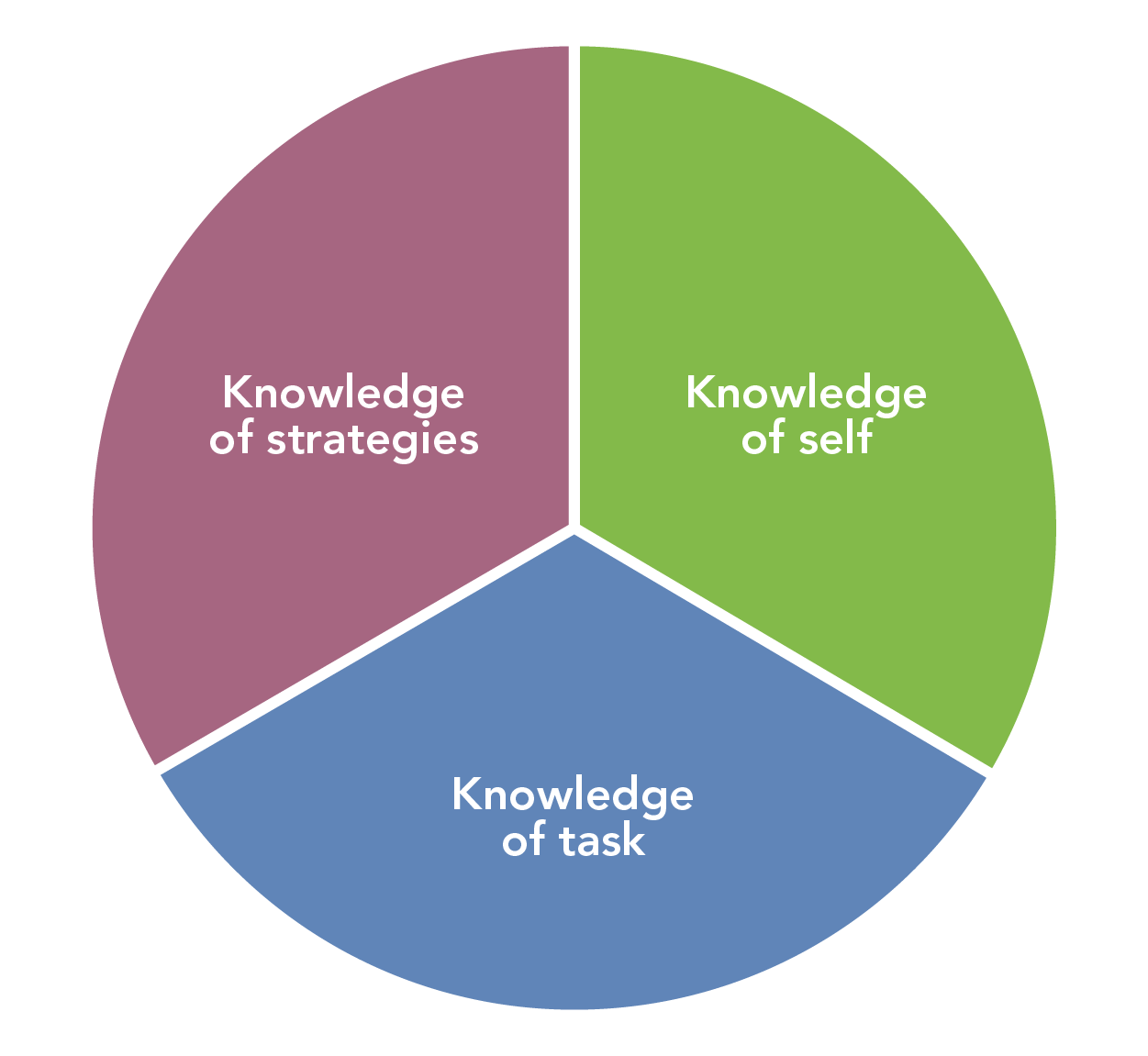
Metacognitive knowledge refers to what learners know about learning. They must have a knowledge of:
- Themselves and their own cognitive abilities (e.g. I find it difficult to remember technical terms)
- Tasks, which may be subject-specific or more general (e.g. I am going to have to compare information from these two sources)
- The range of different strategies available, and an ability to choose the most appropriate one for the task (e.g. If I begin by estimating then I will have a sense of the magnitude of the solution).
Metacognitive knowledge must be explicitly taught within subjects. Where the assessment process works effectively within this the pupils can measure and understand their own learning. This is particularly important for more able learners who are then able to take greater responsibility for their learning, moving this beyond the constraints of the examined curriculum.
The Fisher-Frey Model shows how responsibility for learning moves from teacher to pupils through carefully planned teaching strategies. This model is also relevant to the development of metacognitive teaching strategies as they are developed within schools. The Education Endowment Foundation has shown how the teacher can learn about and teach metacognitive strategies, gradually passing the learning to the pupils.

Diagram based on work of Fisher-Frey and EEF
At each stage some form of assessment takes place to ensure the required or expected outcomes have been achieved. The teacher wants to know the impact of the teaching and the pupils want to know the effectiveness of their learning. The teacher must also assess the pupils’ ability to use metacognitive strategies. Are they simply accepting the situation as it is? Are they attempting to engage in the process but do not know which strategy is best? Are they able to use their learning strategically or have they moved on to become reflective and independent learners? The teacher uses the assessment information with the pupil to help them to become increasingly self-aware and more adept at using the strategies available to them, but also to recognise their own strengths.
Strategies used in metacognitively focused classrooms which can be developed with the teacher’s support, undertaken by pupils and assessed might include:
- Prioritising tasks
- Creating visual models such as bubble maps and flow diagrams
- Questioning
- Clarifying details of the task
- Making predictions
- Summarising information
- Making connections
- Problem solving
- Creating schema
- Organising knowledge
- Rehearsing information to improve memory
- Encoding
- Retrieving
- Using learning and revision strategies
- Using recall strategies
If pupils and teachers work together to assess and plan the process of learning about the things they need to know and about themselves as learners, then metacognitive self-regulation becomes possible. Metacognitive regulation refers to what learners do about learning. It describes how learners monitor and control their cognitive processes. Pupils can then learn through a cyclic process in which they learn how to plan, monitor and evaluate both what they learn and how they learn.

Based on diagram in Getting Started with Metacognition, Cambridge International Education Teaching and Learning Team
Pupils need to know how to work through these crucial stages to be successful in their academic work and in support of their metacognitive processes. For example, a learner might realise that a particular strategy is not achieving the results they want, so they decide to try a different strategy. Assessment information will help them to refine the strategies they use to learn. They will use this to evaluate their subject knowledge, metacognitive knowledge and metacognitive regulation. They will become more motivated to engage in learning and can develop their own strategies and tactics to enhance their learning.
Conclusion: the potential of metacognition to enhance assessment, teaching and learning
If teaching is focused on subject content and only subject content is assessed, then teachers will be able to plan, track, set targets and work towards examination grades.
When a teacher is knowledgeable about cognition and cognitive strategies, teaching and learning becomes more interesting. The teacher begins to share the objectives and success criteria with the pupils. Planning for teaching and the learning activities develop cognition and move beyond simple recall and application of facts. Pupils become more able to use and organise information. They are more able to retain knowledge and use it in a variety of complex or original contexts. The teacher remains in control of the planning, teaching and assessment but pupils have some degree of understanding of this. They are now more able to respond to advice about their learning. They begin to try alternative methods for learning. They know what they are doing well, what they still need to do, how they need to do this and why it is important. They utilise the assessment criteria and feedback to enhance their learning.
Teachers who teach pupils about metacognition and help them to develop metacognitive awareness know the importance of giving control to the pupil. They collaborate with the pupils to assess their development in becoming more strategic or reflective in the use of strategies. Pupils learn better because they begin to assess their own learning strategies and their subject knowledge with a plan, monitor and evaluate model. Their motivation improves and the conversations between teachers and their pupils about learning are more insightful.
Call for contributions: share your school’s experience
In this article I highlight the importance of metacognition for learning and for the learner. I also explain the importance of assessing what is happening in the classroom. Assessment will give the teacher a clear indication of the impact of teaching and the effectiveness of learning. Assessment will help the self-regulated learner to reflect on their learning and develop the strategies needed to be a successful learner throughout life.
We are seeking NACE member schools to contribute to our work in this area by sharing information about effective assessment approaches in their contexts. Where has assessment practice been implicit within your teaching? How was it planned? How did if fit within the teaching? How was the process shared with the pupils? How did you and the pupils measure levels of achievement? How did this change the way they learned or the way you taught?
If you can share examples of the way you have built up assessment processes within the classroom and across the school, we would love to hear from you.
Please contact communications@nace.co.uk for more information, or complete this short online form to register your interest.
Read more: Planning effective assessment to support cognitively challenging learning
Connect and share: join fellow NACE members at our upcoming member meetup on the theme "rethinking assessment" – 23 March 2022 at New College, Oxford – to share ideas and examples of effective assessment practices. Details and booking
References and additional reading
- Anderson, Neil J. (2002). The Role of Metacognition in Second Language Teaching and Learning. ERIC Digest.
- Cahill, H. et al (2014). Building Resilience in Children and Young People: A Literature Review for the Department of Education and Early Childhood Development. DEECD.
- Cambridge International Education Teaching and Learning Team. Getting Started with Metacognition.
- Chick, N. (2013). Metacognition. Centre for Teaching, Vanderbilt University.
- Education Endowment Foundation (2018). Metacognition and Self-Regulated Learning: Seven recommendations for teaching self-regulated learning & metacognition
- EEF. Evidence Summaries: Metacognition and Self-Regulation
- EEF. Four Levels of Metacognitive Learners (Perkins, 1992)
- EEF. Metacognition and Self-Regulated Learning: School Audit Tool
- EEF (Muijs D., Bokhove C., 2020). Metacognition and Self-Regulation Review
- EEF (Quigley, A., Muijs, D., & Stringer, E., 2020). Metacognition & Self-Regulated Learning Guidance Report
- Fisher, D. & Frey, N. (2008). Better Learning Through Structured Teaching: A framework for the gradual release of responsibility. ASCD.
- Lowe, H. and McCarthy, A. (2020). Making Space for Able Learners – Cognitive Challenge: Principles into Practice. NACE.
- Webb, J. (2021). Extract from The Metacognition Handbook. John Catt Educational.
Tags:
assessment
cognitive challenge
feedback
metacognition
myths and misconceptions
pedagogy
progression
questioning
research
Permalink
| Comments (0)
|
  
|
Posted By Keith Watson FCCT,
08 November 2021
|
The opportunities that present themselves to teachers these days are truly amazing. Last summer the chance to write and deliver a Zoom-based programme of learning to primary-aged pupils in Beijing was presented to me. Yes, Beijing. How could I refuse the opportunity to apply an English teaching style to another culture? Through a partnership between NACE and a private educational provider I embarked upon a programme of 16 two-hour sessions over a period of eight weeks via Zoom, using Google Classroom for resources and homework. The lessons were taught from 7-9pm 9pm Beijing time. Would my teaching keep the nine-year olds awake on a Sunday night?
The context
The education company I worked with offers what it terms ‘gifted and talented programmes’ to all ages and across the curriculum. The pupils mainly attended international schools and had their school lessons taught in English. The programmes have previously been delivered in person during the summer holidays by overseas teachers, primarily from the US. A move to Zoom-based learning after the pandemic has proved successful and now lessons are offered throughout the year in the evening and at the weekend with parents paying highly for the courses. The company organised the programme very well with training and support for the teacher at every stage. It is an impressive operation.
I taught an English literature unit based upon a comparative novel study using ‘The Iron Man’ and ‘The Giant’s Necklace’ – texts familiar to many Key Stage 2 teachers. The pupils worked hard in lessons, listened well and thought deeply. They retained knowledge well and I used retrieval practice at the start of most lessons. They completed these tasks eagerly. They were a pleasure to teach. Off-task behaviour was rare, pupils laughed when jokes were made – though of course humour was lost in translation at times (or maybe my jokes were not funny).
What worked?
Central to the learning was the pupils reading aloud. They loved this. It gave me the chance to clarify meaning, check vocabulary and asks questions at depth. All pupils read, some with impressive fluency given it was their second language. Parents commented they were not used to working this way. I think in other courses they often read for homework and then in lessons answered questions at length and then wrote essays. Despite being young there is an emphasis on academic writing. One pupil referred to his story as an essay, revealing that writing a story was unusual for his studies. Writing the story was a highlight for the pupils, one I suspect they are not used to. The reading also allowed for targeted questions, which the parents seemed to like, having not seen the technique used before. Yes, parents often sat next to their child, out of my eyesight, to help if needed. Hearing them whisper what to say on occasion was a new one for me.
To get an idea of the dedication of the pupils and support of the parents, it is worth mentioning that one pupil joined the lesson while travelling home on a train from her holiday. With her mum sat next to her, she joined in the lesson as best she could and all with a smile on her face. Another pupil said her father had asked her how she was reviewing the learning from the previous lesson each week. Learning is valued. Technical difficulties were rare but when they arose the pupils were proactive in overcoming difficulties, moving rooms and logging on with another device. Resilience and self-regulation was noticeably high. The last lesson included a five-minute presentation from each pupil on what they had learned from the unit. Pupils prepared well, the standard was high and pupils showed depth of understanding of the themes covered.
Addressing the language gap
As a teacher the main challenge to emerge was the gap between the pupils’ understanding of complex literary concepts and the use of basic English. The units are aimed at what is termed ‘gifted and talented’ yet at times I needed to cover areas such as verb tenses at a basic level. In English assessment terms the students were at times working at Year 6 greater depth for reading and some aspects of their writing, but were only ‘working towards’ in other areas.
I have decades of experience teaching EAL learners, the majority of whom attained at or above national expectation at the end of Key Stage 2 despite early language challenges. Here the gap was even more pronounced. Should I focus on the higher-order thinking and ignore what was essentially a language issue? I decided not to do that since the students need to develop all aspects of their English to better express their ideas, including writing. I did mini-grammar lessons in context, worked primarily on verb tenses in their writing and when speaking, and prioritised Tier 2 vocabulary since Tier 3 specialist vocabulary was often strong. They knew what onomatopoeia was, but not what a plough was, let alone cultural references like a pasty. Why would they?
Motivations and barriers
At the start of each lesson, I welcomed each pupil personally and asked them, ‘What have you been doing today?’ Almost every answer referred to learning or classes. They had either completed other online lessons, swimming lessons, fencing lessons, piano practice (often two hours plus) or other planned activities. Rarely did a pupil say something like ‘I rode my bike’. Having a growth mindset was evident and the students understood this and displayed admirable resilience. Metacognition and self-regulation were also evident in learning.
However, one area where the pupil did struggle was in self-assessment. The US system is based on awarding marks and grades regularly, including for homework. I chose not to do this, thinking grades for homework would be somewhat arbitrarily awarded unless something like a 10-question model was used weekly. The research on feedback without grades suggests that it leads to greater pupil progress and this was my focus. It would be interesting to explore with the students whether my lack of grade awarding lowered their motivation because they were used to extrinsic rather than intrinsic motivation. Does this contradict my assertion that growth mindset was strong?
Another issue emerged linked to this – that of perfectionism. One pupil was keen to show her knowledge in lessons but was the only pupil who rarely submitted homework. A large part of the programme was to write a story based on ‘The Iron Man’, which this student did not seem to engage with. At the parents’ meeting the mother asked if she could write for her child if it was dictated, a suggestion I rejected saying the pupil needed to write so that I could provide feedback to improve. It became clear the child did not want to submit her work because it was ‘not as good as their reading’. The child had told me in the first lesson that they had been accelerated by a year at school. I fear problems are being stored up that my gentle challenges have only now begun to confront and that may take a long time to resolve. This was not the case for the other pupils, but the idea of pressure to work hard and succeed was always evident. I realise the word ‘pressure’ here is mine and may not be used by others in the same context, including the parents.
Parental support
So, what of parental engagement? The first session began with getting-to-know-each-other activities and a discussion on reading. After 20 minutes the TA messaged me to say the parent of one pupil felt the lesson was ‘too easy’. Nothing like live feedback! I messaged back that the aim at that point was to relax the children and build a teaching relationship. A few weeks later the same parent asked to speak to me at the end of the lesson. I was prepared for a challenge that did not materialise. She said her child liked the lessons and she loved the way I asked personalised questions to extend her child. She was not used to her being taught this way. I used a mixture of cold-calling, named lolly-sticks in a pot and targeted questions, which seemed novel and the children loved.
Parent meetings were held half-way through the unit and feedback about things like the questioning wasvery positive. The extremely upbeat response was surprising since the teaching seemed a little ‘flat’ to me given the limitations of Zoom but that is not how it was received. The pupils seemed to enjoy the variety of pace, the high level of personal attention, the range of tasks, the chunking of the learning and the sense of fun I tried to create. Parents asked when I was delivering a new course and wanted to know when I was teaching again.
Final reflections
So, what did I learn? Children are children the world over, which we all know deep down. But these children apply themselves totally to their work. They expect to work hard and enjoy ‘knowing’ things. Their days are filled with activity and learning. Zoom can work well but still the much-prized verbal feedback is not the same from 5,000 miles away.
And finally, as a teacher I have learned over the years to be professional and to keep teaching whatever happens. When a pupil said they didn’t finish their homework because they were traveling back home, I enquired where they had been. ‘Wuhan’ they replied. Without missing a beat, I further asked, ‘So what do you think about the plot in chapter two then?’
Would you be interested in sharing your experiences of teaching remotely and/or across cultures? Is this an area you’d like to explore or develop? Contact communications@nace.co.uk to share your experience or cpd@nace.co.uk to express your interest in being part of future projects like this.
Tags:
feedback
language
literature
lockdown
mindset
motivation
parents and carers
pedagogy
perfectionism
questioning
remote learning
vocabulary
Permalink
| Comments (0)
|
  
|
Posted By Ann McCarthy,
06 October 2021
|
NACE Research & Development Director Dr Ann McCarthy shares key principles for effective assessment planning and practice, within cognitively challenging learning environments.
Following two academic years of uncertainty and alternative arrangements for teaching and assessment, the conversation regarding testing and assessment has become increasingly important. Upon return to the routines of day-to-day classroom teaching, schools have had to find ways to assess knowledge, progress and understanding achieved through distance learning or redesigned classroom practices. For older pupils there has been a need to provide evidence to examination boards to secure grades and guarantee appropriate progression routes. This inherent need to provide checks and balances before pupils’ achievement is recognised can become a distraction from the art of teaching. In fact, Rimfield et al (2019) found a very high agreement between teacher assessments and exam grades in English, maths, and science.
- Could we examine less often and use classroom-based assessment more often?
- Should we rethink testing and assessment and their position in the learning process?
Testing vs assessment
The terms test and assessment are often used interchangeably, but in the context of education we need to recognise the difference. A test is a product which is not open to interpretation; it uses learning objectives and measures success achieved against these. Teachers use tests to measure what someone knows or has learned. These may be high-stakes or low-stakes events. High-stakes tests may lead to a qualification, grading or grouping, whereas low-stakes tests can support cognition and learning. Testing takes time away from the process of learning and as such testing should be used sparingly, when necessary and when it contributes significantly to the next steps in teaching or learning.
Assessment, by contrast, is a systematic procedure which draws on a range of activities or evidence sources which can then be interpreted. Regardless of the position teachers hold regarding the use of testing and examinations, meaningful assessment remains an essential part of teaching and learning. Assessment sits within curriculum and pedagogy, beginning with diagnostic assessment to plan learning which best reflects the needs of the learner. A range of formative assessment activities enable the teacher and pupils to understand progress, improve learning and adapt the learning to reflect current needs. Endpoint activities can be used as summative assessments to appreciate the degree to which knowledge has been acquired, alongside varied and complex ways in which that knowledge can be used.
Assessment might be viewed in three different ways: assessment of learning; assessment for learning; and assessment as learning. The choice of assessment practice will then impact on its use and purpose. Regardless of the process chosen and the procedures used, the teacher must remember that the value of the assessment is in the impact it has on pedagogy and practice and the resulting success for the pupils, rather than as an evidence base for the organisation.
NACE research has shown that cognitively challenging experiences – approaches to curriculum and pedagogy that optimise the engagement, learning and achievement of very able young people – will have a significant and positive impact on learning and development. But how can we see this working, and what role does assessment play? When planning for cognitively challenging learning, assessment planning should reflect the priorities for all other aspects of learning.

A strategic approach to assessment which supports cognitively challenging learning environments
When considering the place of assessment in education, teachers must be clear about:
- What they are trying to assess;
- How they plan to assess;
- Who the assessment is for;
- What evidence will become available;
- How the evidence can be interpreted;
- How the information can then be used by the teacher and the pupil;
- The impact the information has on the planned teaching and learning;
- The contribution assessment makes to cognition, learning and development.
Effective assessment is integral to the provision of cognitively challenging learning experiences. With careful and intentional planning, we can assess cognitive challenge and its impact, not only for the more able pupils, but for all pupils. Assessments are used to measure the starting point, the learning progression, and the impact of provision. When working with more able pupils, in cognitively challenging learning environments, the aim is to extend assessment practices to include assessment of higher-order, complex and abstract thinking.
When used well, assessment provides the teacher with a detailed understanding of the pupils’ starting points, what they know, what they need to know and what they have the potential to do with their learning. The teacher can then plan an engaging and exciting learning journey which provides more able pupils with the cognitive challenge they need, without creating cognitive overload.
The Education Endowment Foundation (EEF) has joined with others to recognise the importance of cognitive science to inform interventions and classroom practice. Spaced learning, interleaving, retrieval practice, strategies to manage cognitive load and dual coding all support cognitive development – but are dependent on effective assessment practices which guide the teaching and learning. The best assessment methods are those that integrate fully within curriculum teaching and learning.
Assessment and classroom management
It is important to place the learner at the centre of any curriculum plan, classroom organisation and pedagogical practice. Initially the teacher must understand the pupils’ strengths and weaknesses, together with the skills and knowledge they possess, before engaging in new learning. This understanding facilitates curriculum planning and classroom management, which have been recognised as essential elements of cognitively challenging learning. Often, learning time is lost through additional testing and data collection, but when working in cognitively challenging environments, planned learning should be structured to include assessment points within the learning rather than devising separate assessment exercises.
When assessing cognitively challenging learning, pupils need opportunities to demonstrate their abilities using analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. They must also show how they use their existing knowledge in new, creative, or complex ways, so questions might include opportunities to distinguish between fact and opinion, to compare, or describe differences. The problems may have multiple solutions or alternative methodologies. Alternatively, pupils may have to extend learning by combining information shared with the class and then adding new perspectives to develop ideas.
Assessing cognitively challenging learning will also include measures of pupils’ abilities to think strategically and extend their thinking. Strategic thinking requires pupils to reason, plan, and sequence as they make decisions about the steps needed to solve problems, and assessment should measure this ability to make decisions, explain solutions, justify their methods, and obtain meaningful answers. Assessments which demonstrate extended thinking will include investigations, research, problem solving, and applications to the real world. Pupils’ abilities to extend their thinking can be observed through problems with multiple conditions, a range of sources, or those drawn from a variety of learning areas. These problems will take pupils beyond classroom routines and previously observed problems. Assessment at this level does not depend on a separate assessment task, but teaching and learning can be reviewed and evaluated within the learning process itself.
Assessment in language-rich learning environments
Language-rich learning environments support cognitive challenge, high-order thinking and deep learning for more able pupils. It is therefore inevitable that language, questioning and dialogic discourse are key elements of formative assessment. They allow the teacher to assess learning in the moment and adjust the course of learning to adapt to the needs of the pupils.
Assessment in the moment, utilising effective questions and dialogic discourse, does not happen by accident, but is planned into the learning. When planning a lesson, the big ideas and essential questions which will expose, extend and deepen the learning are central to the planning and assessment. When posing the planned questions or creating opportunities for discourse, pupils need time to formulate their ideas and think before discussing the responses and extending learning with their own questions and ideas.
Within the language-rich classroom where an understanding of assessment is shared with pupils, the ownership of learning can be passed to them. The teacher will introduce the theory, necessary linguistic skills, and technical language, using these to model good questions and questioning techniques. More able pupils will develop their own oracy, language and questioning techniques, and then develop them together. Through regular practice and good classroom routines, pupils gain the confidence and skills to ask ‘big questions’ themselves and engage in dialogue. At this point, discussion and questioning becomes an effective mode of ongoing assessment. As pupils explain their thinking, misconceptions or gaps in knowledge will be exposed, allowing the teacher to assess, support learning, and encourage deeper thinking.
Priorities for effective assessment
Within the classroom, the teacher needs to use assessment:
- To understand what the pupils know already;
- To promote and sustain cognitive challenge and progression:
- To measure the impact of both the teaching and the learning;
- To adapt practice in a timely manner;
- To support, extend and enhance learning;
- To examine how effectively the knowledge is used in new, varied and complex contexts.
Assessment has the potential to support pupils as learners as they will:
- Understand the nature and purpose of activities so that they can benefit from them;
- Appreciate the demands of learning;
- Engage in the learning journey;
- Develop their own cognitive skills and learning attributes;
- Take action to improve themselves;
- Take ownership of learning;
- Become increasingly autonomous and self-regulating.
Assessment is not a separate part of teaching and learning, but should be planned within the teaching. Assessment should not distract pupils from learning, and learning should not be framed to meet assessment criteria. Assessment is not about data gathering and organisational checks, but it should lead to enriched learning and refined practice with teachers and pupils working together to achieve an exciting learning environment.
What next?
This year, NACE is focusing on exploring effective assessment practices within Challenge Award-accredited schools. We hope that many schools will participate in this project, to provide evidence and share examples of effective assessment: what works, how, and why? By sharing our expertise with others we can move the conversation about assessment forwards and provide exciting and engaging learning for our pupils. To find out more or to express your school’s interest in contributing to this initiative, please contact communications@nace.co.uk
References
- Education Endowment Foundation (2021), Cognitive science approaches in the classroom (a review of the evidence)
- Rimfield. K, et.al. (2019), Teacher assessment during compulsory education are as reliable, stable, and heritable as standardized test scores. The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 60(12) (1278-1288)
Read more:
Tags:
assessment
cognitive challenge
feedback
myths and misconceptions
oracy
progression
questioning
research
Permalink
| Comments (2)
|
  
|
Posted By Keith Watson FCCT,
22 March 2021
|
Dr Keith Watson, NACE Curriculum Development Director
What I Talk About When I Talk About Running by Haruki Murakami is one of my favourite books… even if reading it did not make me run faster. The title did, however, lead me to ask students: “What do you think about when you think about learning?” This is not an easy question to answer. We increasingly recognise the importance of developing metacognition in learning and the need to challenge pupils cognitively, but this is not always easy in the mixed ability classroom.
In the NACE report Making space for able learners – Cognitive challenge: principles into practice (2020), cognitive challenge is defined as “ how learners become able to understand and form complex and abstract ideas and solve problems”. We want students to achieve these high ambitions in their learning, but how is this achieved in a mixed ability class with increasing demands on the teacher, including higher academic expectations? The NACE report provides case studies showing where this has been achieved and highlights the common features across schools that are achieving this – and these key themes are worth reflecting upon. What do we mean by “challenge for all”?
“Challenge for all” is the mantra often recited, but is it a reality? At times it can appear that “challenge” is just another word for the next task. Or, perhaps, just a name for the last task. Working with teachers recently I asked: why do the more able learners need to work through all the preceding the tasks to get to the “challenge”? Are you asking them to do other work that is not challenging? Or coast until it gets harder? A month later the same teachers talked about how they now move those learners swiftly on to the more challenging tasks, noting that their work had improved significantly, they were more motivated and the learning was deeper. This approach also led to learners being fully engaged, meaning the teacher could vary the support needed across the class to ensure all pupils were challenged at the appropriate level.
“Teaching to the top” is another phrase widely used now and it is a good aspiration, although at times it is unclear what the “top” is. Is it grade 7 at GCSE or perhaps greater depth in Year 6? It is important to have these high expectations and to expose all learners to higher learning, but we need to remember that some of our learners can go even higher but also be challenged in ways that do not relate to exams. For instance, at Copthorne Primary School, the NACE report notes that “pupils are regularly set complex, demanding tasks with high-level discourse. Teachers pitch lessons at a high standard”. Note the reference to discourse – a key feature of challenge is the language heard in the classroom, whether from adults or learners. The “top” is not merely a grade; it is where language is rich and learning is meaningful, including in early years, where we often see the best examples.
Are your questions big enough?
The use of “low threshold, high ceiling” tasks are helpful in a mixed ability class, with all pupils able to access the learning and some able to take it further. In maths, a question as simple as “How many legs in the school?” can lead to good outcomes for all (including those who realise the question doesn’t specify human legs). But there is often a danger that task design can be quite narrow. The minutiae of the curriculum can push teachers to bitesize learning, which can be limiting – especially when a key aim has to be linking the learning through building schema. Asking “Big Questions” can extend learning and challenge all learners. The University of Oxford’s Oxplore initiative offers a selection of Big Questions and associated resources for learners to explore, such as “Should footballers earn more than nurses?” and “Can money buy happiness?”. There is a link to philosophy for children here, and in cognitively challenging classrooms we see deep thinking for all pupils. Can your learners build more complex schema?
All pupils need to build links in their learning to develop understanding, and more able learners can often build more detailed schema. To give a history example, understanding the break from Rome at the time of Henry VIII could be learned as a series of separate pieces of knowledge: marriage to Catherine of Aragon, the need for a male heir, wanting a divorce in order to marry Anne Boleyn, the religious backdrop, etc. Knowing these items is one thing, but learners need to make links between them and create a schema of understanding. The more able the pupil, the more links can be made, again deepening understanding. That is why in cognitively challenging classrooms skilled teachers ask questions such as:
- What does that link to?
- What does that remind you of?
- When have you seen this before?
- What is this similar to? Why?
These questions are especially useful in a busy mixed ability classroom. Prompt questions like these can be used in a range of situations, rather than always requiring another task for the more able pupil who has “finished”. (As if we have ever really finished)
Are you allowing time for “chunky” problems?
So, what else provides challenge? The NACE report notes: “At Portswood Primary School pupils are given ill-structured problems, chunky problems, and compelling contexts for learning”. Reflecting upon the old literacy hour, I used to joke: “Right Year 5, you have 20 minutes to write like Charles Dickens. Go!” How could there be depth of response and high-level work in such short time scales? What was needed were extended tasks that took time, effort, mistakes, re-writes and finally resolution. The task often needed to be chunky. Some in the class will need smaller steps and perhaps more modelling from the teacher, but for the more able learners their greater independence allows them to tackle problems over time.
This all needs organising with thought. It does not happen by accident. With this comes a sense of achievement and a resolution. Pupils are challenged cognitively but need time for this because they become absorbed in solving problems. This also works well when there are multiple solution paths. In a mixed ability class asking the more able to find two ways to solve a problem and then decide which was the most efficient or most effective can extend thinking. It also calls upon higher-order thinking because they are forced to evaluate. Which method would be worth using next time? Why? Justify. This also emphasises the need to place responsibility with the learner. “At Southend High School for Boys, teachers are pushed to become more sophisticated with their pedagogy and boost pupils’ cognitive contribution to lessons rather that the teacher doing all the work”. In a mixed ability class this is vital. How hard are your pupils working and, more importantly, thinking?
I wrote in a previous blog post about how essential the use of cutaway is in mixed ability classes. Retrieval practice, modelling and explanation are vital parts of a lesson, but the question is: do all of the students in your class always need to be part of that? A similar argument is made here. More able learners are sometimes not cognitively challenged as much in whole-class teaching and therefore, on occasion, it is preferable for these pupils to begin tasks independently or from a different starting point.
As well as being nurturing, safe and joyful, we all want our classrooms to be cognitively challenging. This is a certainly not easy in a mixed ability class but it can be achieved. High expectations, careful task design and an eye on big questions all play a part, alongside the organisation of the learning. In this way our teaching can be improved significantly – far more than my running ever will be…
Related blog posts
Additional reading and support
Tags:
cognitive challenge
grouping
metacognition
problem-solving
questioning
research
Permalink
| Comments (0)
|
  
|
Posted By Keith Watson FCCT,
08 March 2021
|
Dr Keith Watson, NACE Curriculum Development Director and former CEO of Portswood Primary Academy Trust
“I once estimated that, if you price teachers’ time appropriately, in England we spend about two and a half billion pounds a year on feedback and it has almost no effect on student achievement.”
– Dylan Wiliam
So why do we do it? Primarily because the EEF toolkit identified feedback as one of the key elements of teaching that has the greatest impact. With this came the unintended consequence of an Ofsted handbook and inspection reports that criticised a lack of written feedback and response to pupils’ responses to marking which led to what became an unending dialogue with dangerous workload issues. At some point triple-marking seemed more about showing a senior leader or external inspector that the dialogue had happened. More recently, the 2016 report of the Independent Teacher Workload Review Group noted that written marking had become unnecessarily burdensome for teachers and recommended that all marking should be driven by professional judgement and be “meaningful, manageable and motivating”.
So what is “meaningful, manageable and motivating” in terms of marking and feedback for more able learners? Is it about techniques or perhaps more a question of style? At Portswood Primary Academy Trust our feedback has always been as close to the point of teaching as possible. It centres on real-time feedback for pupils to respond to within the lesson. Paul Black was kind enough to describe it as “marvellous” when he visited, so not surprisingly this is what we have stuck with. Teachers work hard in lessons to give this real-time feedback to shape learning in the lesson. The importance of this approach is that feedback is instant, feedback is relevant, and feedback allows pupils to make learning choices (EEF marking review 2016). But is there more to it for more able learners?
Getting the balance right
In giving feedback to more able learners the quality of questioning is crucial. This should aim to develop the higher-order skills of Bloom’s Taxonomy (analysing, evaluating and creating). A more facilitative approach should develop thinking. The questions should stimulate thought, be open, and may lead in unexpected directions.
A challenge for all teachers is how to balance feeding back to the range of attainment in a class. The recent Ofsted emphasis on pupils progressing through the programmes at the same rate is not always the reality for teachers. Curriculum demands are higher in core subjects, meaning teachers are under pressure to ensure most pupils achieve age-related expectations (ARE). The focus therefore tends to be more on pupils below ARE, with more time and effort focused there. The demands related to SEND pupils can also mean less teacher time devoted to more able pupils who have already met the standards.
Given that teachers may have less time for more able learners it is vital the time is used efficiently. For the more able it is less about the pupils getting the right answer, and more about getting them to ask the right questions. Detailed feedback in every lesson is unlikely so teachers should:
- Look at the week/unit as a whole to see when more detailed focus is timely;
- Use pre-teaching (such as in assembly times) to set up more extended tasks;
- Develop pupils’ independence and resilience to ensure there is not an over-reliance on the teacher;
- Identify times in lessons to provide constructive feedback to the more able group that would have the most impact.
Another tension for teachers is the relationship between assessment frameworks and creativity. For instance, at KS1 and KS2, the assessment criteria at greater depth in writing is often focused on technical aspects of writing. But is this stifling creativity? Is the reduction in students taking A-level English because of the greater emphasis on the technical at GCSE? As one able Year 10 writer commented, “Why do I have to focus on semicolons so much? Writing comes from the heart.” Of course the precise use of semicolons can aid writing effectively from the heart, but if the passion is dampened by narrow technical feedback will the more able child be inspired to write, paint or create? Teachers need to reflect on what they want to achieve with their most able learners.
Three guiding principles
So what should the guiding principles for feedback to more able learners be? Three guiding principles for teachers to think about are:
1. Ownership with responsibility
More able learners need to take more ownership of their work; with this comes responsibility for the quality of their work. Self-marking of procedural work and work that has a definitive answer (the self-secretary idea) allows for children to:
- Check – “Have I got it?”
- Error identify – “I haven’t got it; here's why”
- Self-select to extend – “What will I choose to do next?”
Only the last of these provides challenge. The first two require responsibility from learners for the fundamentals. The third leads to more ownership for pupils to take their learning further. The teacher could aid this self-selection or only provide feedback once a course of action is taken. Here the teacher is nudging and guiding but not dictating with their feedback.
2. Developing peer assessment
There is a danger that peer assessment can be at a low level so the goal is developing a more advanced level of dialogue about the effectiveness of outcomes and how taking different approaches may lead to better outcomes or more efficient practice. For instance, peer feedback allows for emotional responses in art/design/computing work – “Your work made me feel...”; “This piece is more effective because...”. For some more able pupils not all feedback is welcome, whether from peers or teachers. The idea that I can reject your feedback here is important: “Can you imagine saying to Dali that his landscapes are good but he needs to work on how he draws his clocks?”
3. Being selective with feedback
The highly skilled teacher will, at times, decide not to give feedback, at least not straight away. They are selective in their feedback. If you jump in too quickly, it can stop thinking and creativity. It can eliminate the time to process and discover. It can also be extremely annoying for the learner!
In practical terms this means letting them write in English and giving feedback later, not while they are in the flow. In a mathematical/scientific/humanities investigative setting, let them have a go and ask the pertinent question later, perhaps when they encounter difficulty. This question will be open and may nudge rather than direct the pupils. It might not be towards your intended outcome but should allow for them to take their learning forward, perhaps in unexpected directions.
In summary, this gets to the heart of the difference in feedback for more able learners compared to other pupils. While the feedback will inevitably have higher-level subject content, it should also:
- Emphasise greater responsivity for the pupil in their learning
- Involve suggestion, what ifs and hints rather than direction, and…
- Seek to excite and inspire to occasionally achieve the fantastic outcome that a more rigid approach to feedback never would. They may even write from the heart.
What does this look like in practice?
Jeavon Leonard, Vice Principal at Portswood Primary School, outlines a personal approach for more able learners he has used: “Think about when we see a puzzle in a paper/magazine – if we get stuck (as adults) we tend to flip to the answer section, not to gain the answer alone but to see how the answer was reached or fits into the clues that were given. This in turn leads to a new frame of skills to apply when you see the next problem. If this is our adult approach, why would it not be an effective approach for pupils? The feedback is in the answer. Some of the theory for this is highlighted in Why Don't Students Like School? by Daniel Willingham.”
Mel Butt, NRICH ambassador and Year 6 teacher at Tanners Brook Primary, models the writing process for her more able learners including her own second (and third) drafts which include her ‘Think Pink’ improvement and corrections. While this could be used for all pupils, Mel adds the specific requirements into the improved models for more able learners based on the assessment requirement framework for greater depth writing at the end of Key Stage 2. She comments: “I would also add something extra that is specific to the cohort of children based on the needs of their writing. We do talk about the criteria and the process encourages independence too. It's also good for them to see that even their teachers as writers need to make improvements.” The feedback therefore comes in the form of what the pupils need to see based on what they initially wrote.
Further reading
From the NACE blog:
Additional support
Dr Keith Watson is presenting a webinar on feedback on Friday 19 March 2021, as part of our Lunch & Learn series. Join the session live (with opportunity for Q&A) or purchase the recording to view in your own time and to support school/department CPD on feedback. Live and on-demand participants will also receive an accompanying information sheet, providing an overview of the research on effective feedback, frequently asked questions, and guidance on applications for more able learners. Find out more.
Tags:
assessment
differentiation
feedback
metacognition
pedagogy
questioning
Permalink
| Comments (0)
|
|